Full Fix: 0x0000002F INSTRUCTION_BUS_ERROR Blue Screen of Death
7 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help MSPoweruser sustain the editorial team Read more
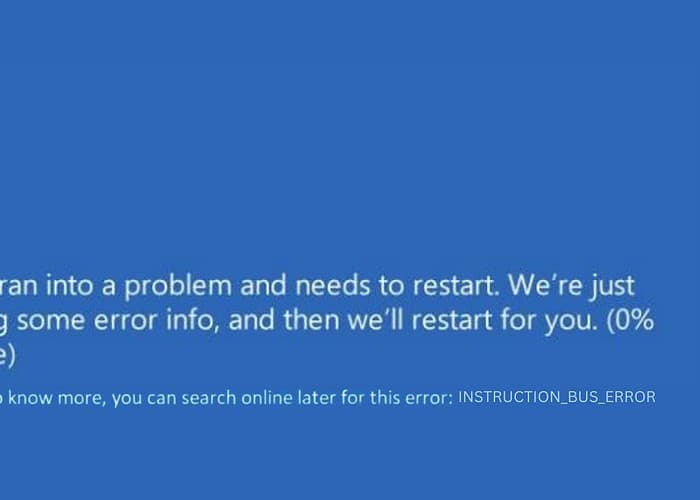
Encountering the 0x0000002F INSTRUCTION_BUS_ERROR Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) was challenging. It was a sudden halt to my daily work.
Through extensive research and testing various solutions, I have compiled a set of effective methods to address this error. In this guide, I share my experience and insights to help you resolve 0x2F.
What Is 0x2F Blue Screen of Death Error?
The 0x2F BSOD, known as INSTRUCTION_BUS_ERROR, is a critical Windows error signaling a problem with the system’s communication with its hardware. It’s typically associated with issues in the data transmission between the system’s processor and other hardware components.
Imagine your computer trying to send instructions to its hardware components, but the message gets lost or corrupted along the way. This disruption can cause the system to crash, leading to BSOD.
What Causes INSTRUCTION_BUS_ERROR?
The INSTRUCTION_BUS_ERROR can be triggered by a variety of issues:
- Faulty Hardware Components: Problems with RAM, motherboard, or other critical hardware.
- Driver Conflicts: Outdated or corrupted drivers interfering with system operations.
- Corrupted System Files: Essential system files getting damaged or corrupted.
- Overheating of Components: Excessive heat causing system instability.
- Power Supply Issues: Inadequate or fluctuating power supply to the system.
- Malware Infections: Viruses or malware that affect system communication.
How To Fix INSTRUCTION_BUS_ERROR Blue Screen of Death?
If the following troubleshooting steps are too much for you, try the BSOD repair tool.
1. Preliminary Checks
Restart Your PC
- Make sure to save any open work before restarting.
- Use the Start menu to reboot your PC.
- Observe if the BSOD reappears after the restart.
Unplug and Plug the External Hardware
- Completely turn off your computer.
- Remove all external devices connected to your PC.
- Restart your PC without the external devices and check if the BSOD persists. Reconnect the devices one by one to identify any conflicts.
2. Restart the PC in Safe Mode
Safe Mode in Windows starts your PC with minimal drivers and services to diagnose and resolve various system issues.
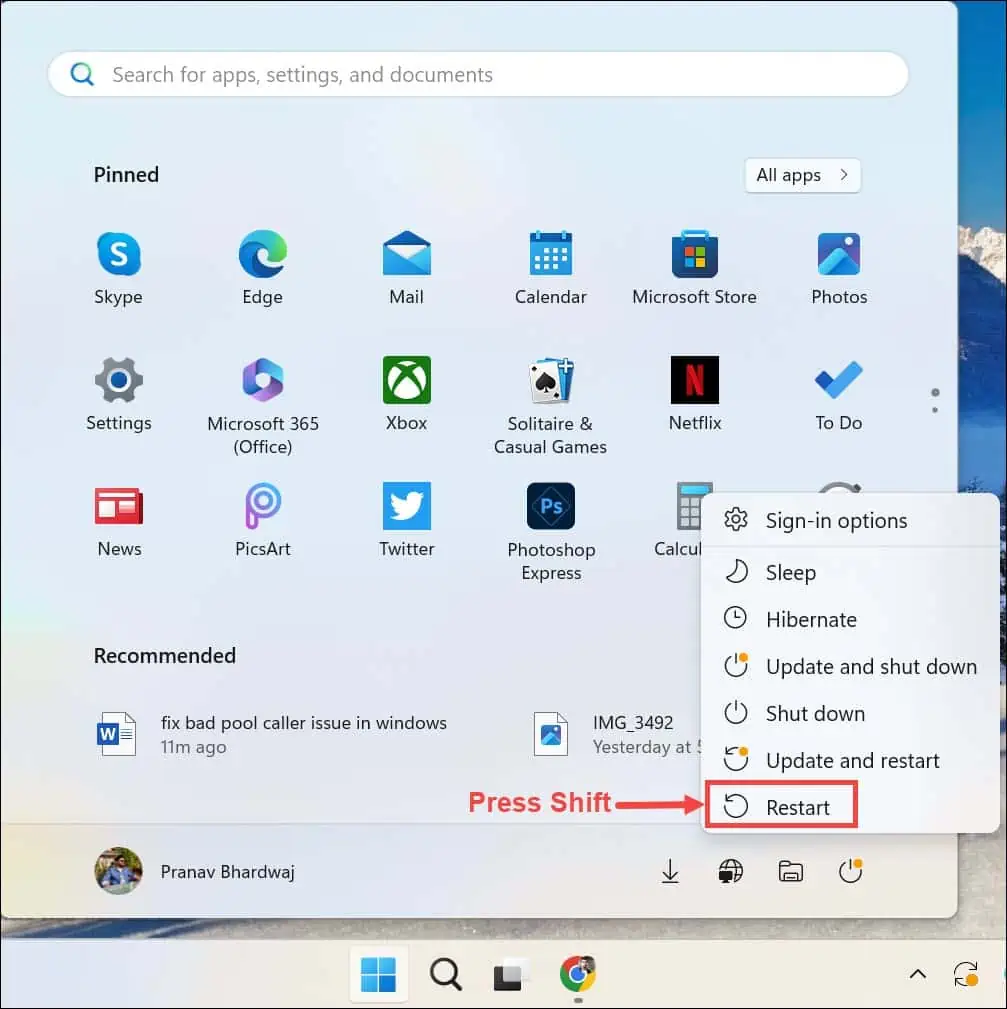
- Open the Start Menu, press and hold the Shift key, and then choose the Power icon followed by the Restart option.
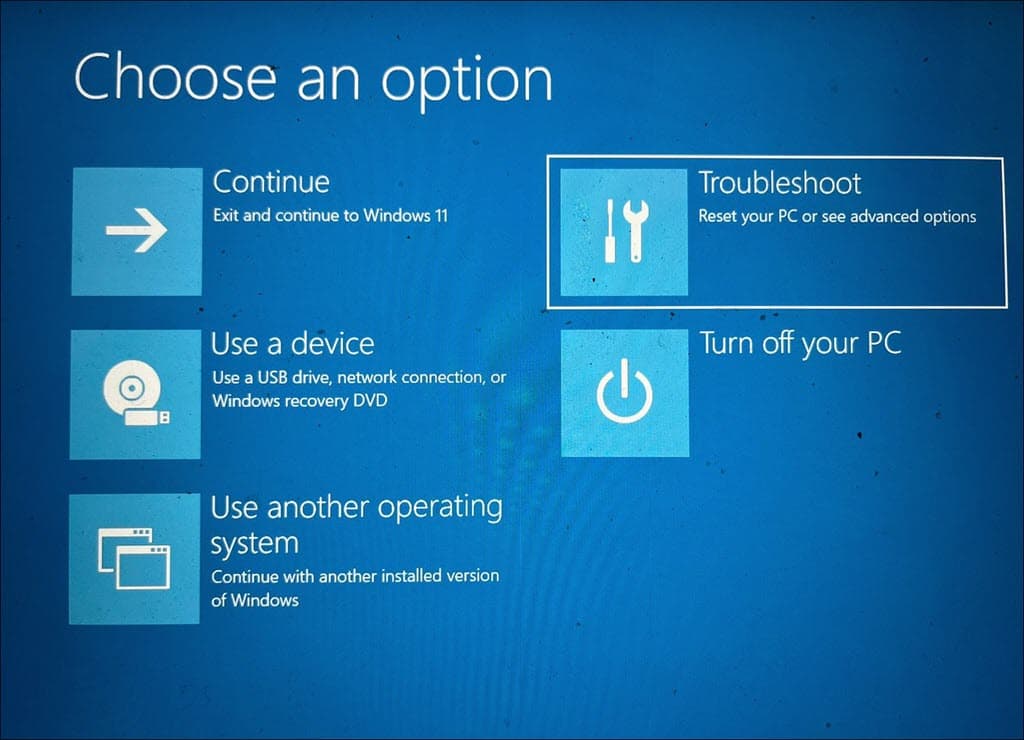
- After your system restarts, select Troubleshoot.
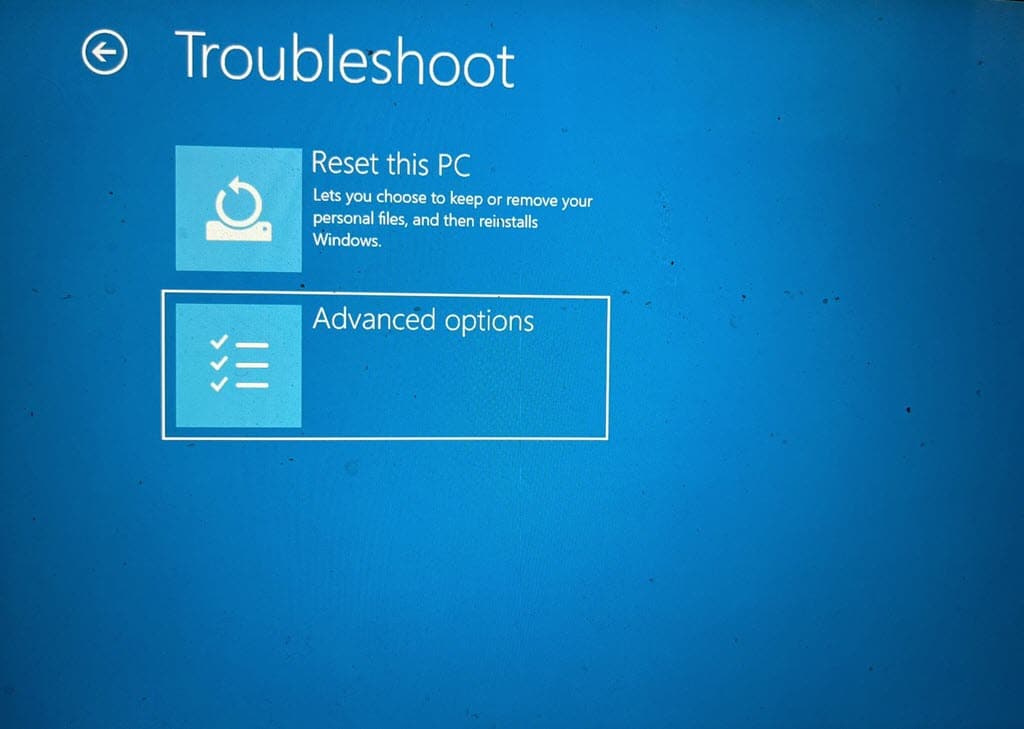
- Then, go to Advanced options.
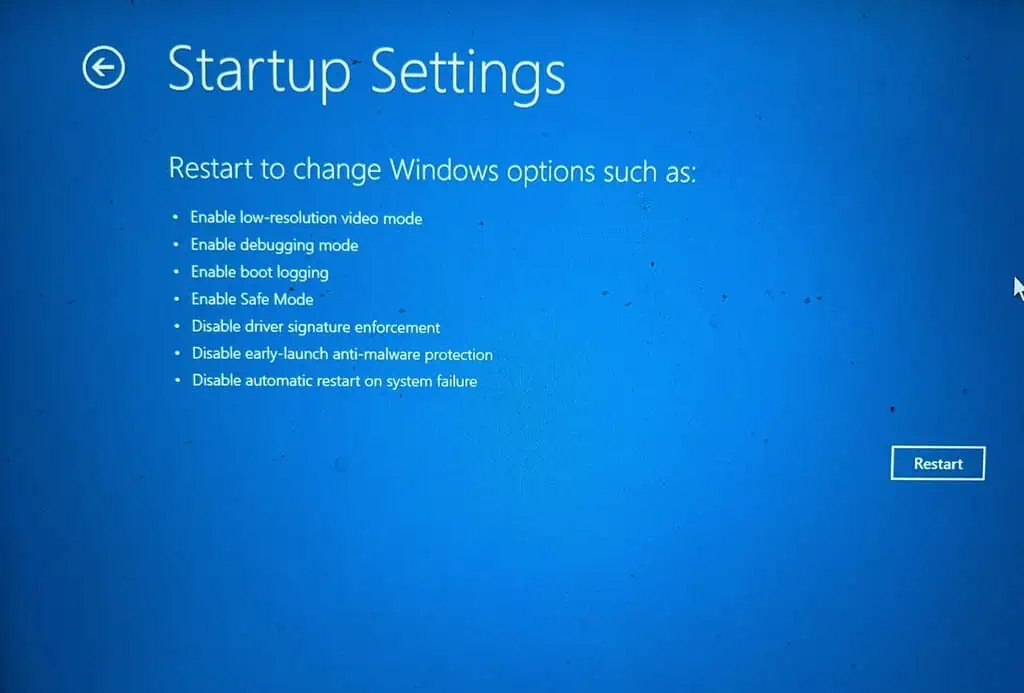
- In Advanced options, select Startup Settings.
- On the next screen, click the Restart button.
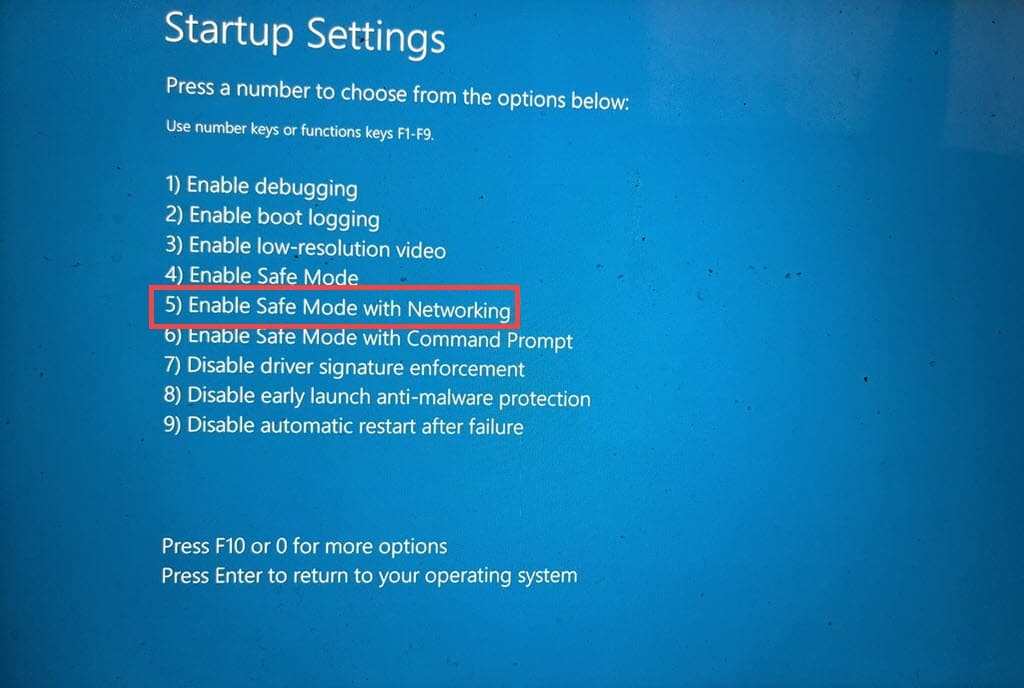
- When your system restarts, press F5 on your keyboard to boot Windows in Safe Mode with Networking.
- Your system should now be operating in Safe Mode.
3. Run SFC and DISM Commands
System File Checker (SFC) and Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) are tools for repairing corrupted system files in Windows.
- Search for “Command Prompt” or “Terminal” in the Start menu, right-click it, and choose Run as administrator.
- Type
sfc /scannowand press Enter. The System File Checker (SFC) will start scanning and repairing any corrupted system files. This might take some time. - Once the SFC scan is complete, type
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealthand press Enter. - After running these commands, restart your computer to make sure all changes are implemented.
Alternatively, you can accomplish this task by using dedicated software. I recommend Fortect because it can run an in-depth scan of your system and identify all the problems. Afterward, this tool will replace all broken files automatically with genuine and clean ones from its verified database, eliminating any room for error when handling sensitive system files.
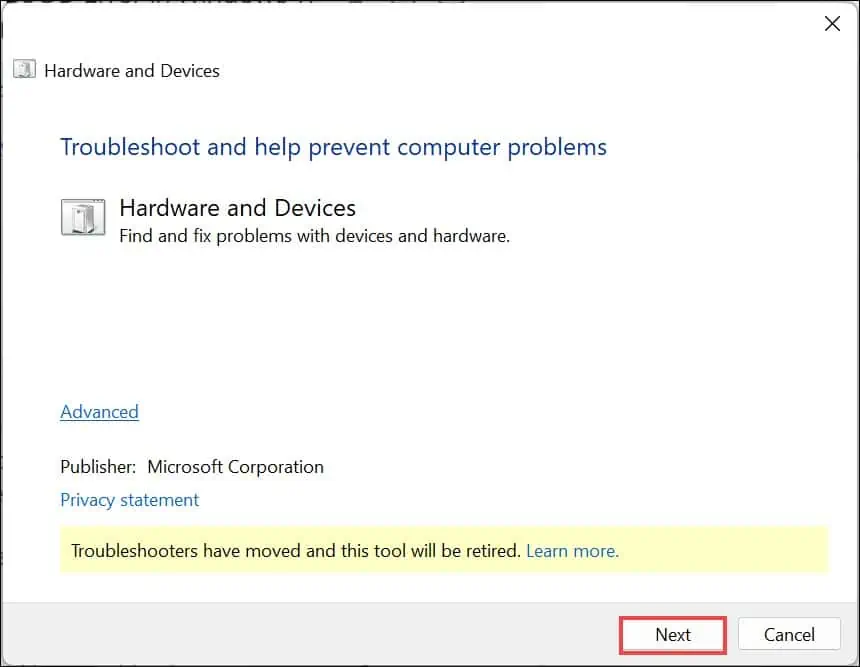
4. Run the Hardware and Device Troubleshooting Tool
Windows includes built-in tools for diagnosing and fixing hardware-related issues, which can be useful in resolving the 0x0000002F INSTRUCTION_BUS_ERROR.
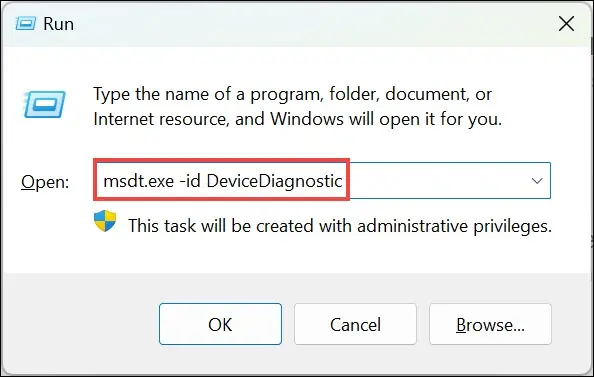
- Press Windows + R to open the Run Command window.
- Type in or copy and paste the command
msdt.exe -id DeviceDiagnosticand then press Enter. - Click Next to initiate the troubleshooting process.
- Windows will start scanning for hardware-related issues.
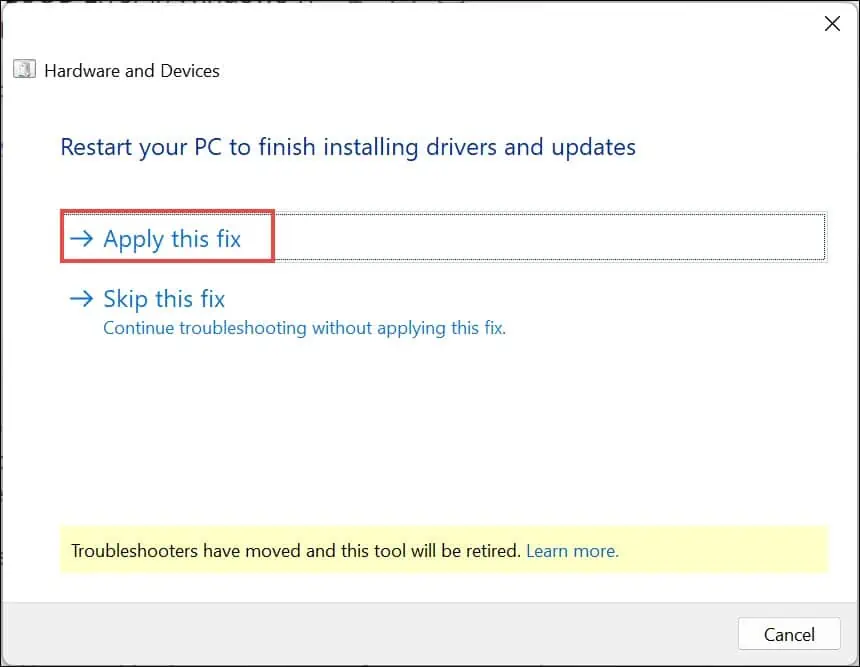
- If any problems are detected, click on Apply this fix.
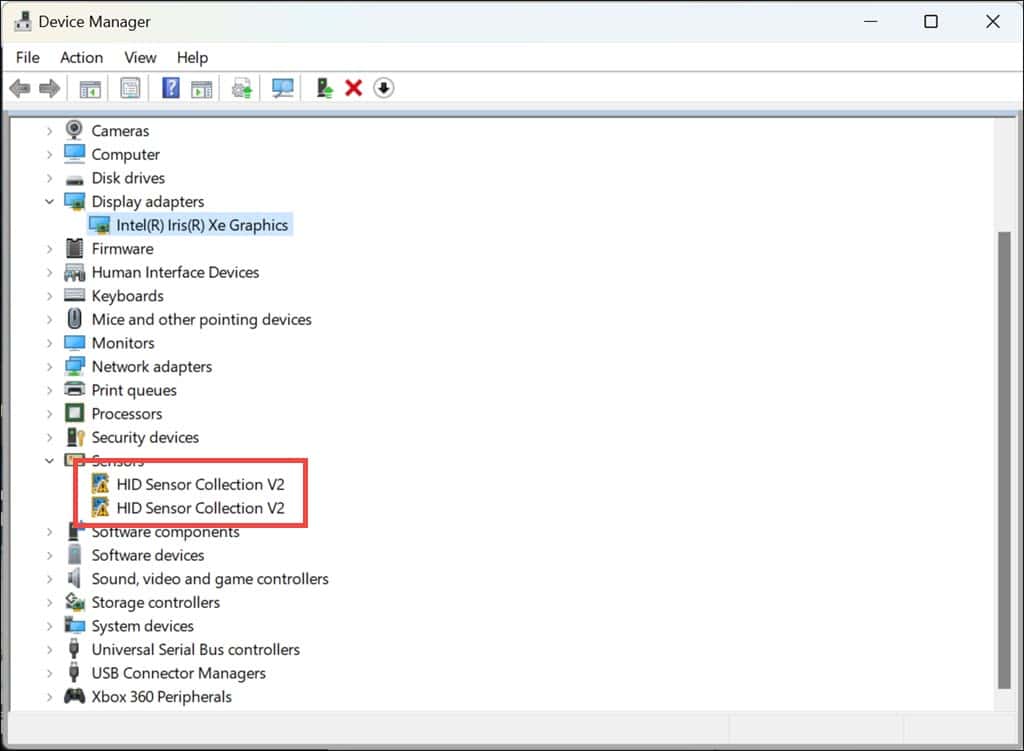
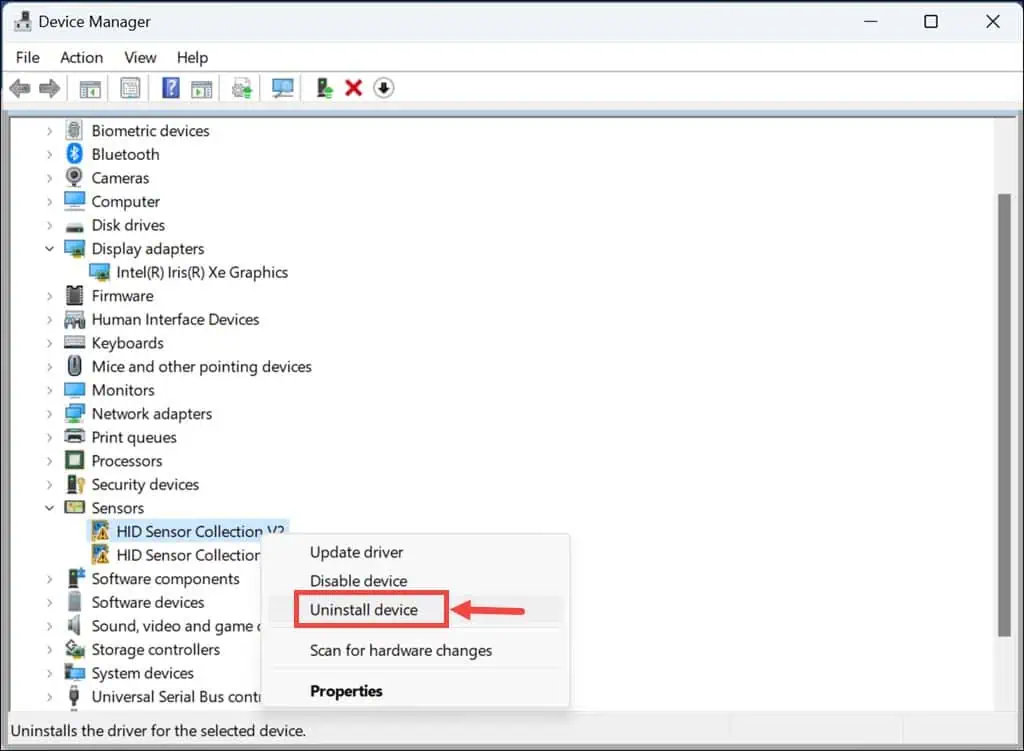
5. Uninstall Corrupted Drivers
- Right-click on the Start button and select Device Manager from the menu.
- In the Device Manager window, identify drivers that display yellow exclamation or warning signs.
- Right-click on each and select Uninstall device.
- Confirm the uninstallation when prompted.
- After completing these steps, restart your PC to apply the changes.
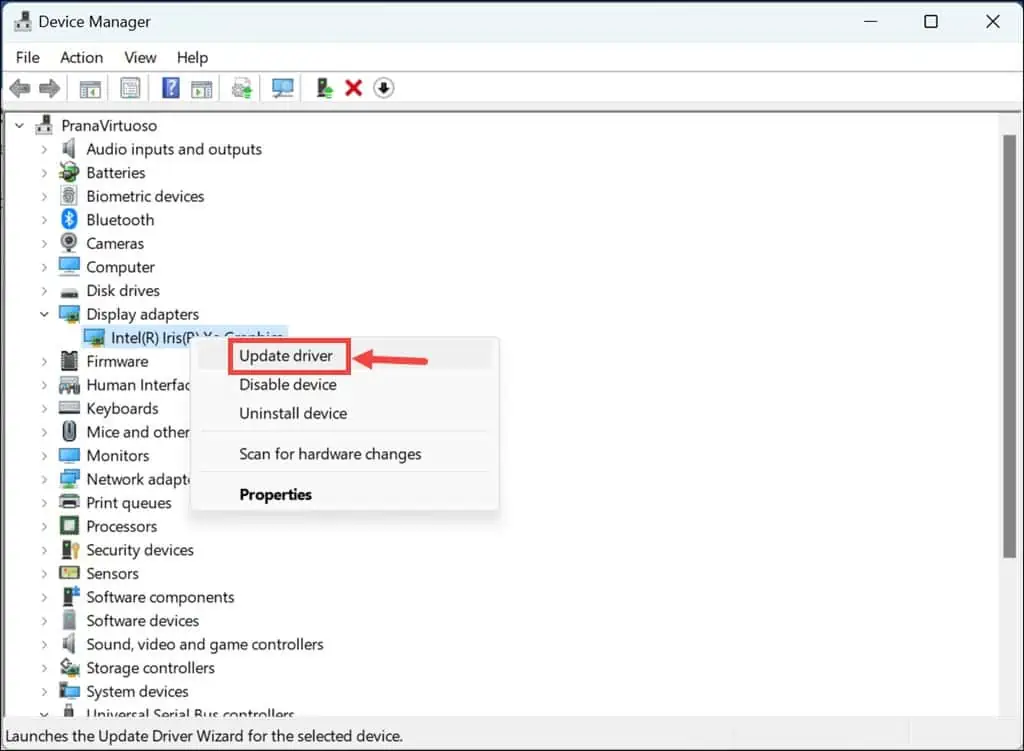
6. Update Essential Drivers
Keeping your system drivers updated is crucial for the proper functioning of your PC and can prevent BSOD errors.
- Right-click on the Start button and choose Device Manager.
- In the Device Manager window, find important drivers such as those for display, firmware, and disk drives.
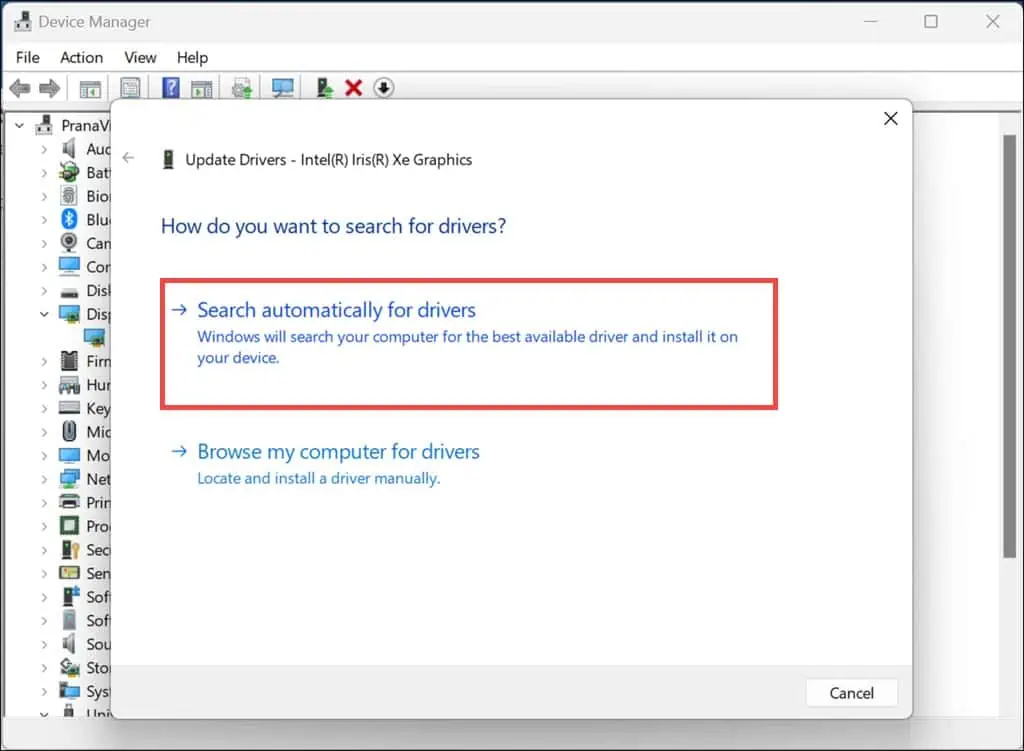
- Right-click on each and select Update driver.
- Choose “Search automatically for drivers” to let Windows handle the driver updates automatically.
- Repeat this procedure for all key drivers, and then restart your computer to make sure the updates are applied.
7. Uninstall Recent Windows Updates
Occasionally, new Windows updates can introduce system instabilities that may lead to BSODs.
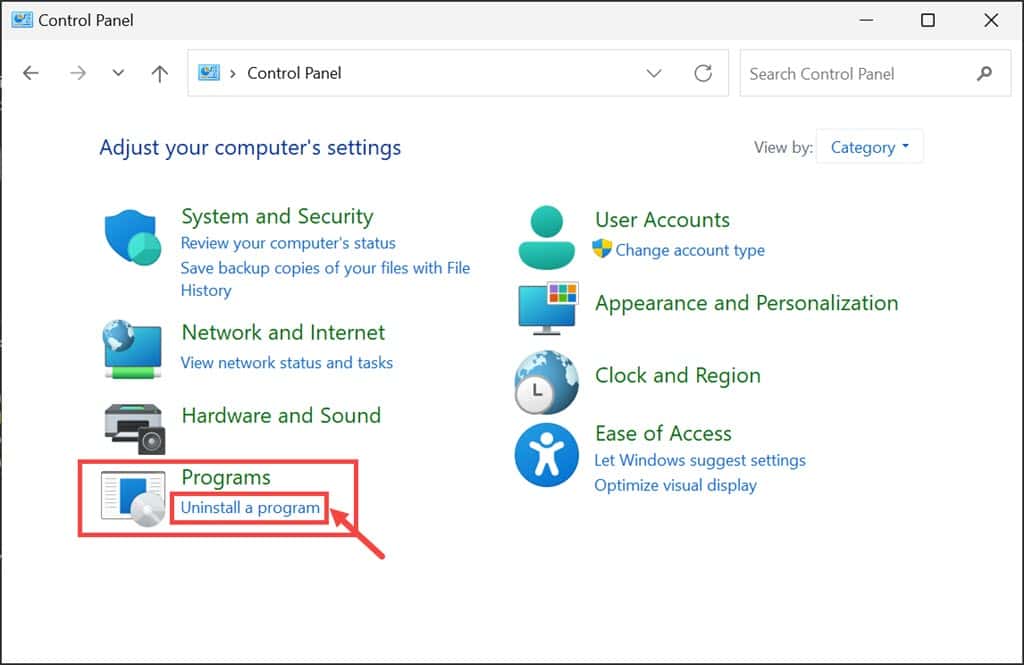
- Enter “Control Panel” in the Windows search box and open it by clicking on its icon.
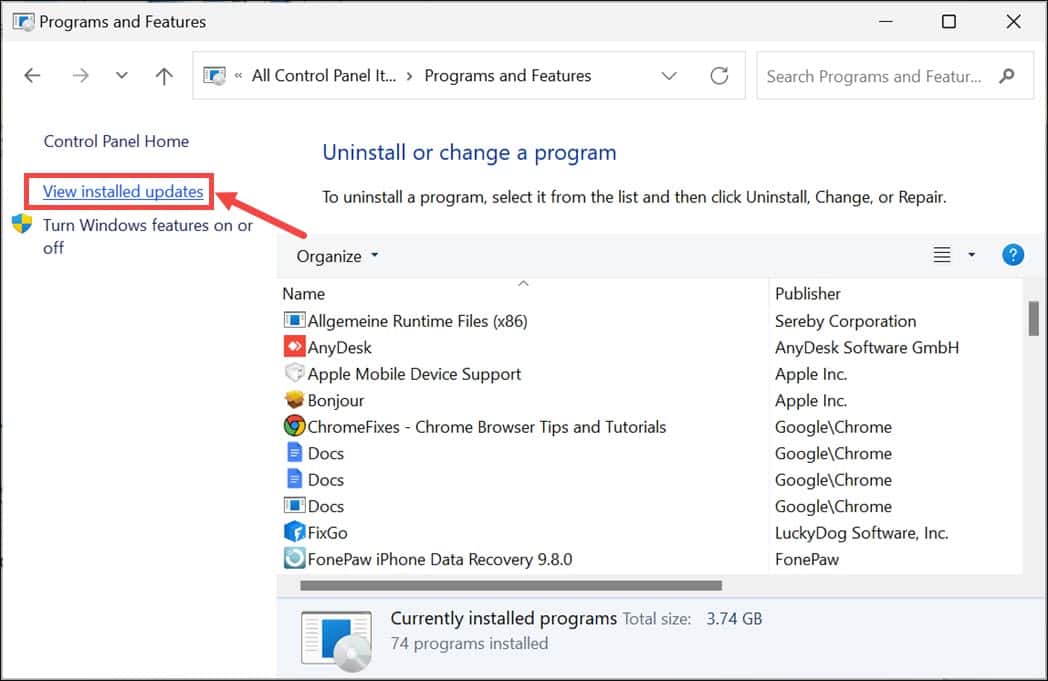
- In the Control Panel, navigate to the “Programs” section and click on Uninstall a program.
- On the left side, select View installed updates.
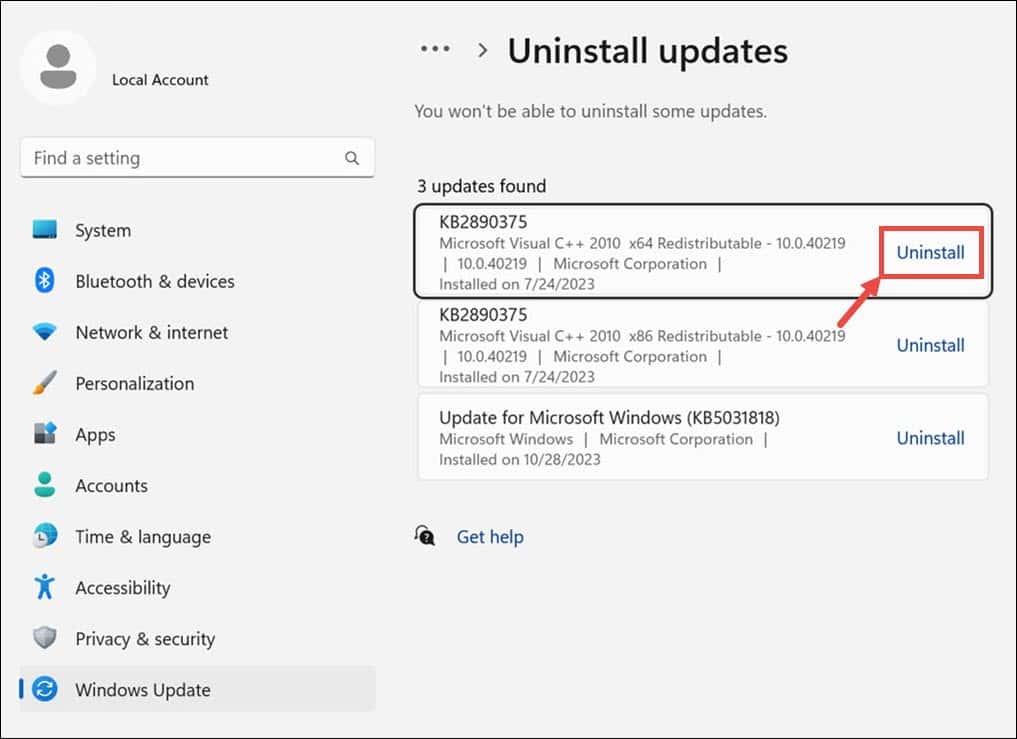
- Find and choose any recently installed updates, then click the Uninstall button.
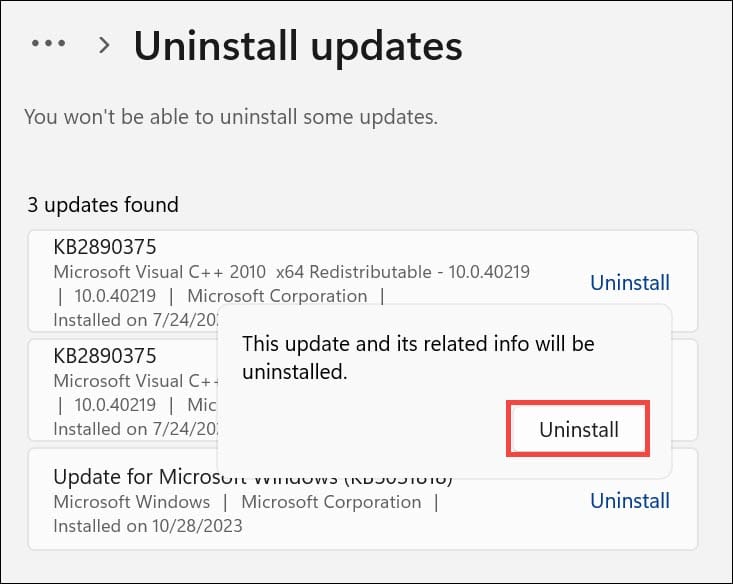
- In the confirmation pop-up, click Uninstall again.
8. Scan for Malware
Malware infections can corrupt system files and drivers, leading to BSODs.
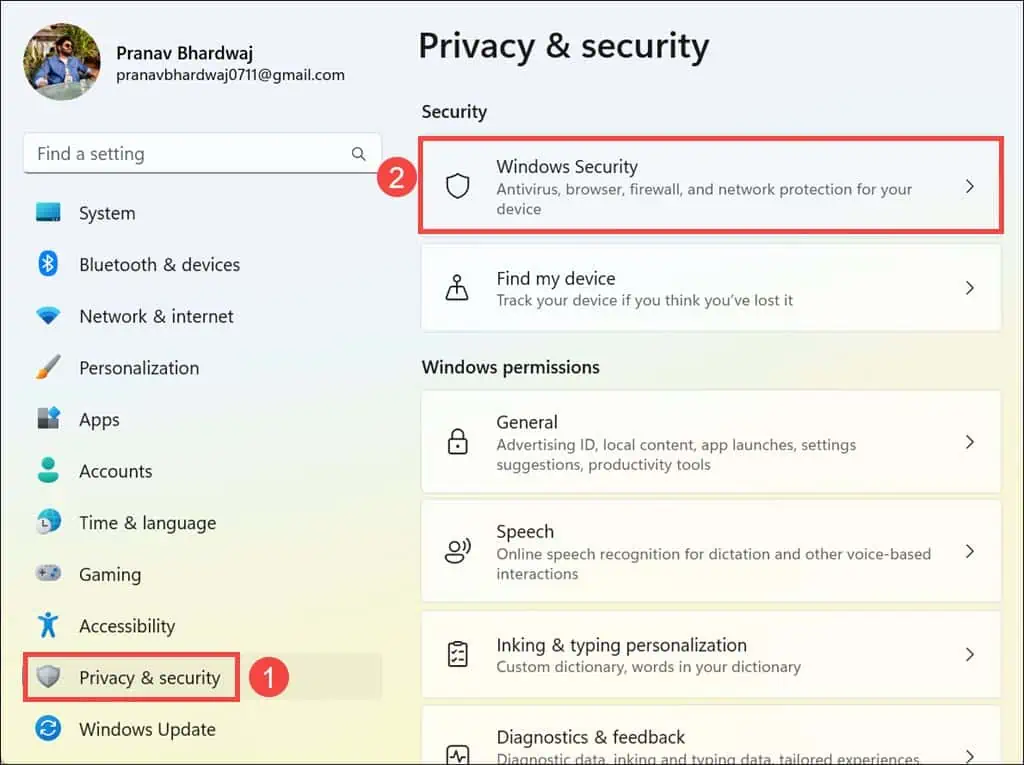
- Press Windows + I to open the Windows settings.
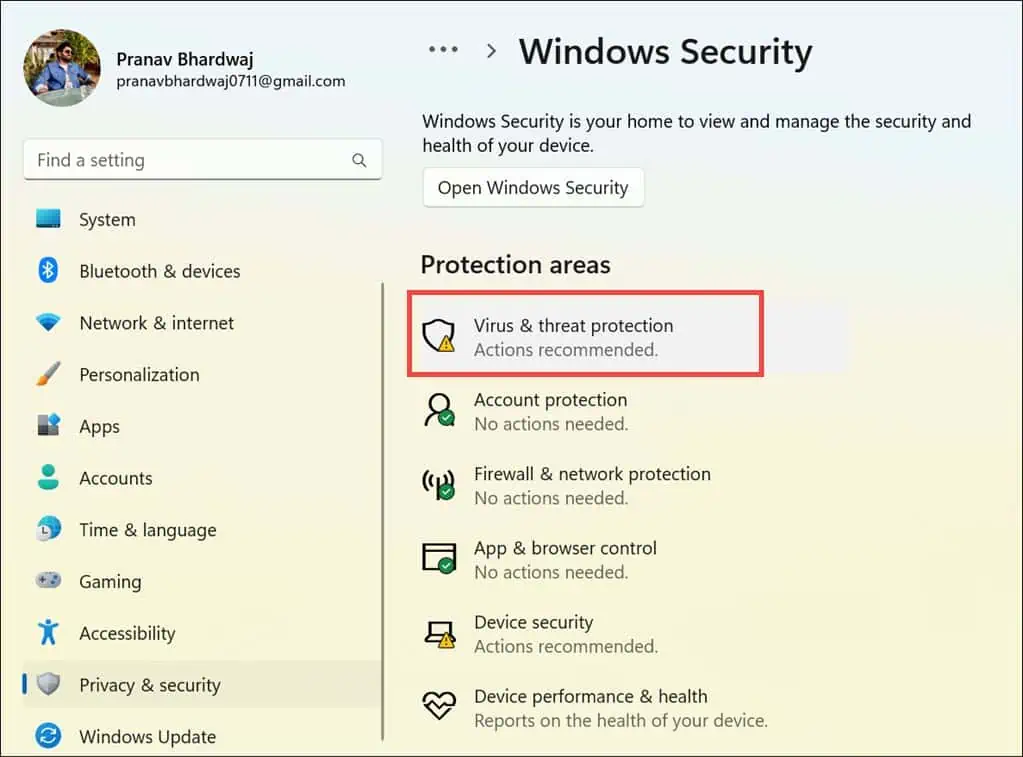
- Within the settings, go to the Privacy & security section on the left, then click on Windows Security on the right.
- In “Windows Security,” select the Virus & threat protection option.
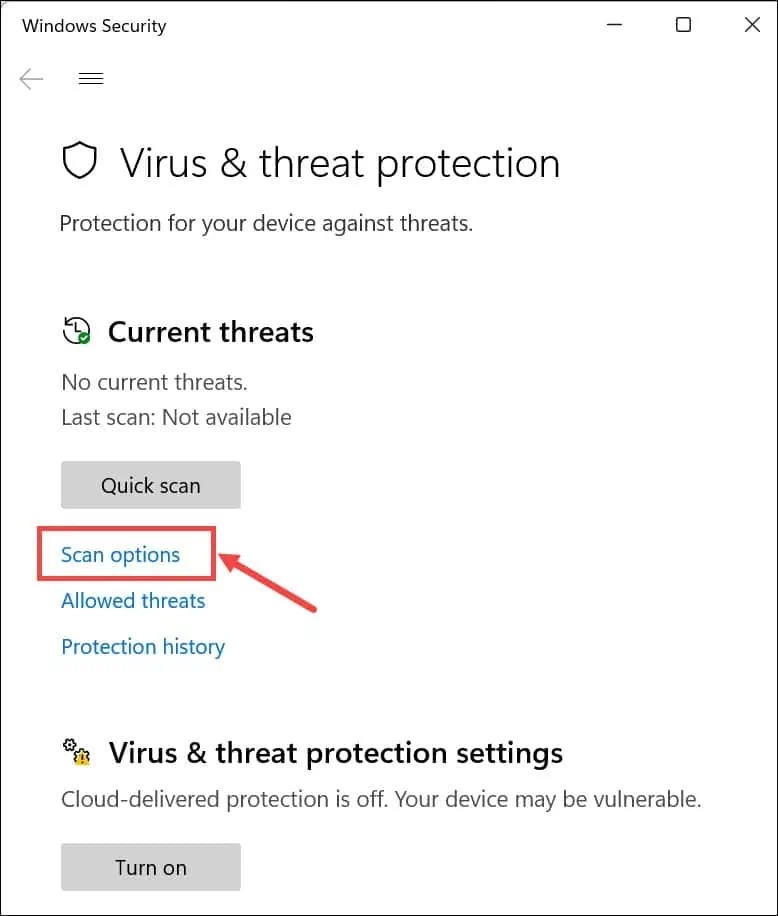
- Click on Scan options.
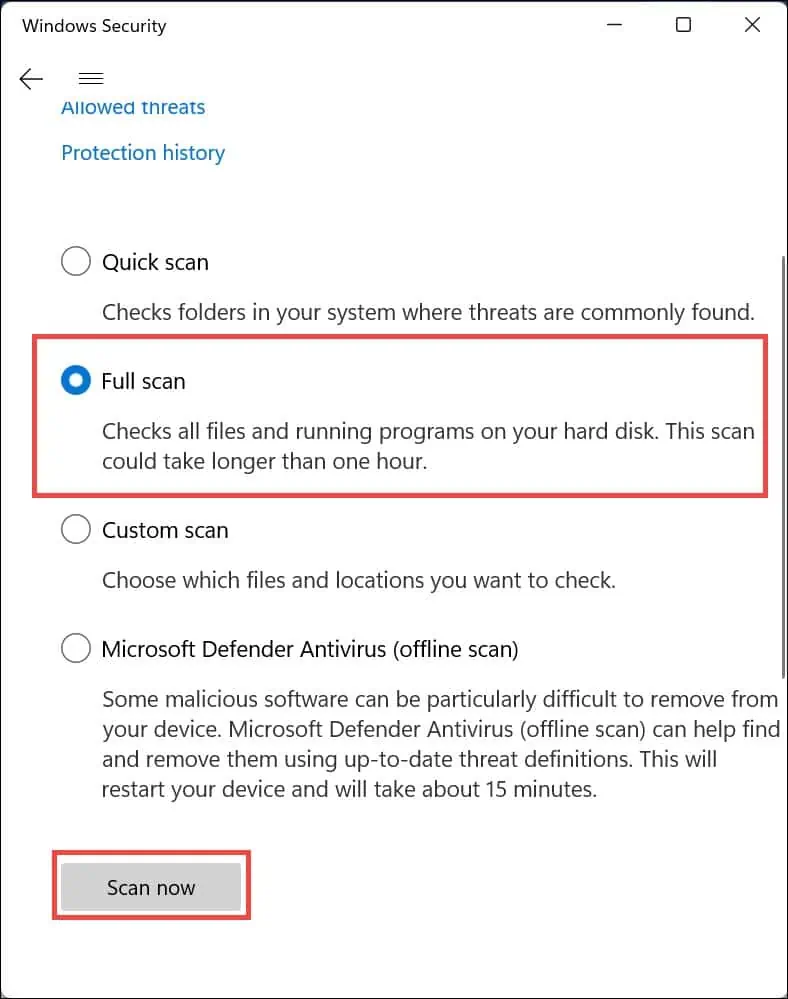
- Select Full scan and then click the Scan now button.
9. Restore Windows to a Previous State
Using Windows System Restore to revert your system to a previous state can resolve BSODs caused by recent changes to the system.
- Restart your system several times until it enters Automatic Repair Mode.
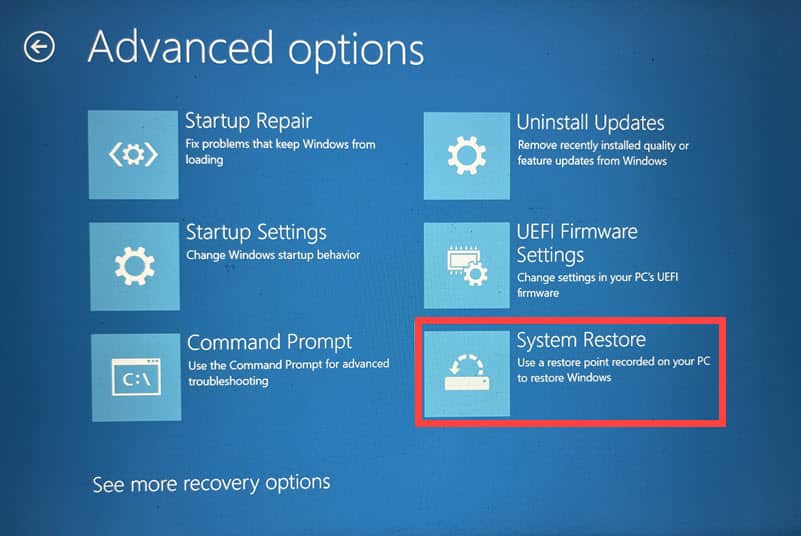
- Once in Automatic Repair Mode, go to the Advanced options menu and select System Restore.
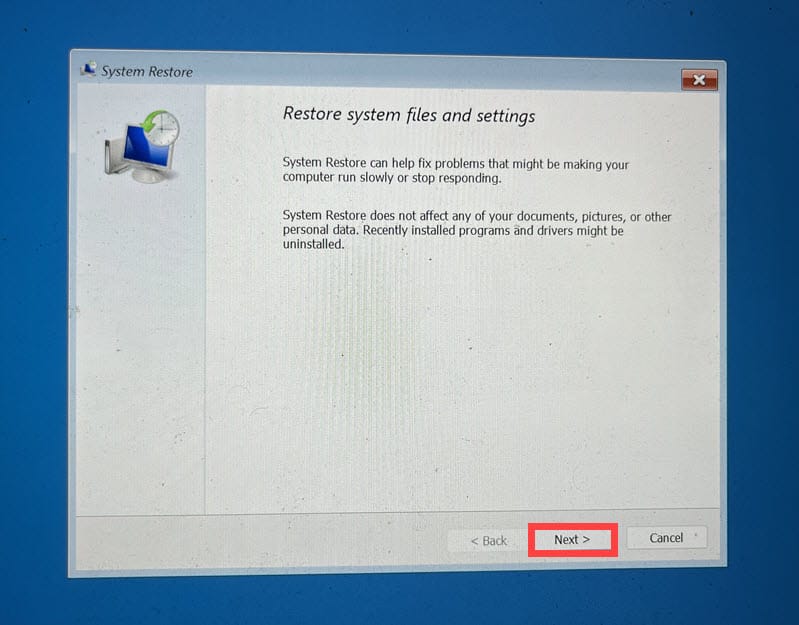
- Click Next to begin the restoration process.
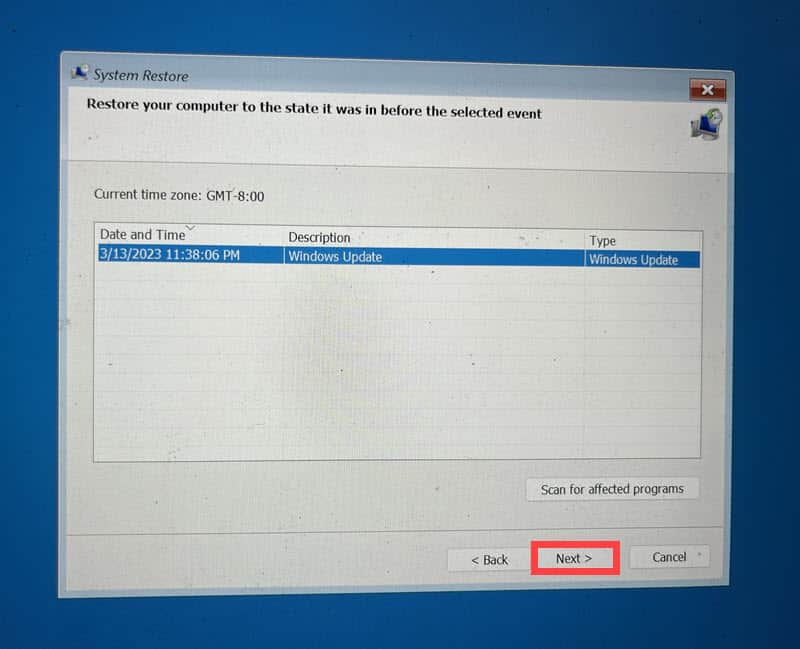
- Select a restore point from a period before the error occurred.
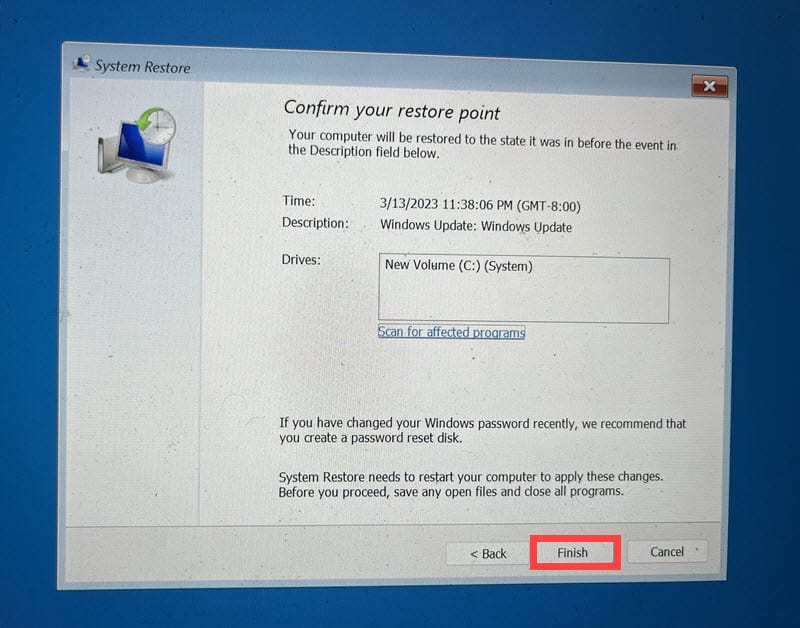
- Confirm your choice of the restore point and click Finish.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the system restoration process.
10. Reset Windows
As a final resort, resetting Windows can help resolve persistent system issues by reinstalling the operating system.
- Keep restarting your PC until it boots into Automatic Repair Mode.
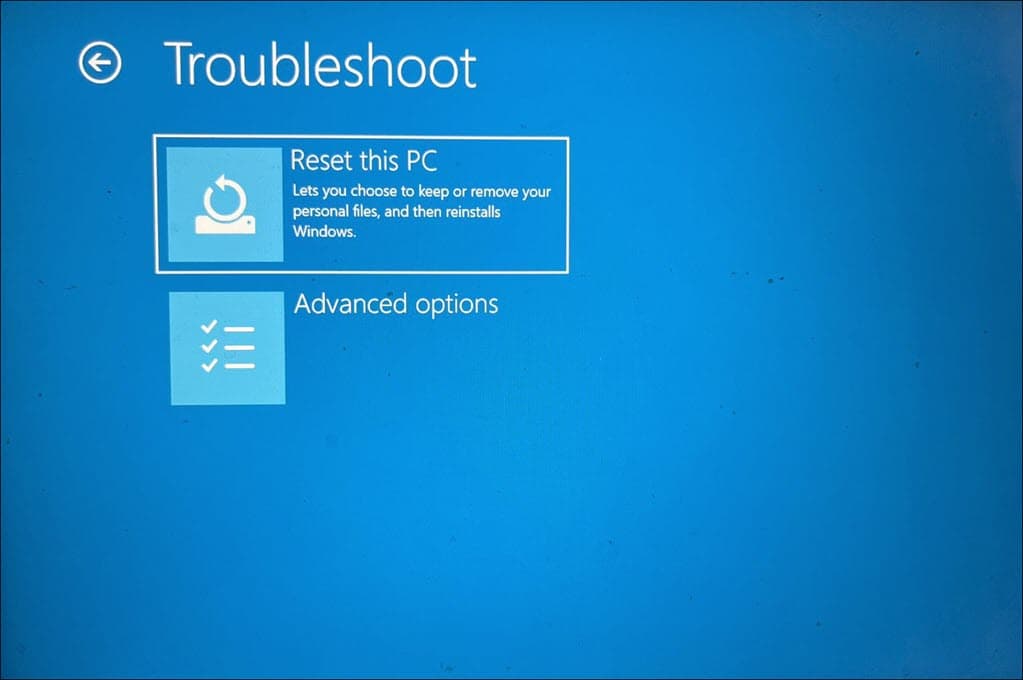
- Once in Automatic Repair Mode, choose the Troubleshoot option.
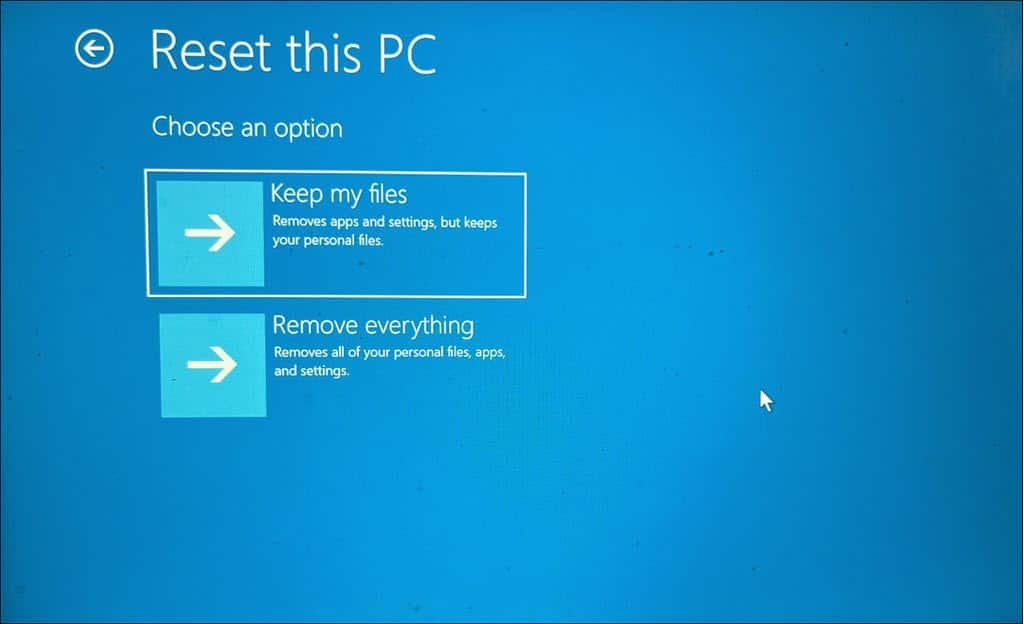
- Inside the “Troubleshoot” menu, select Reset this PC.
- You can either keep your files or remove everything. For a comprehensive reset, opt for Remove everything.
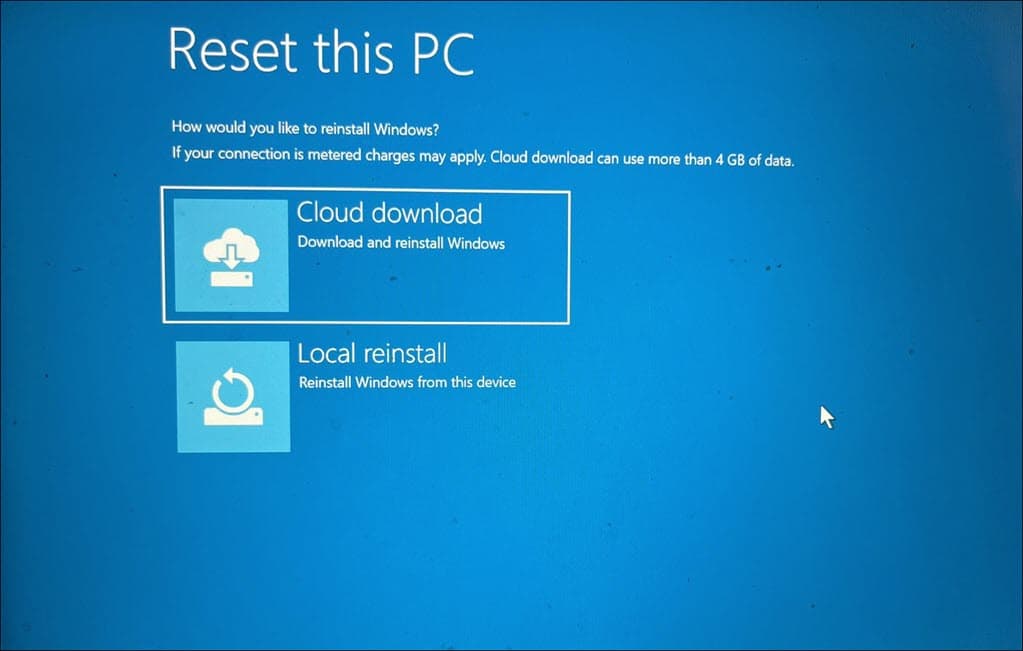
- Next, choose your preferred method for reinstalling Windows.
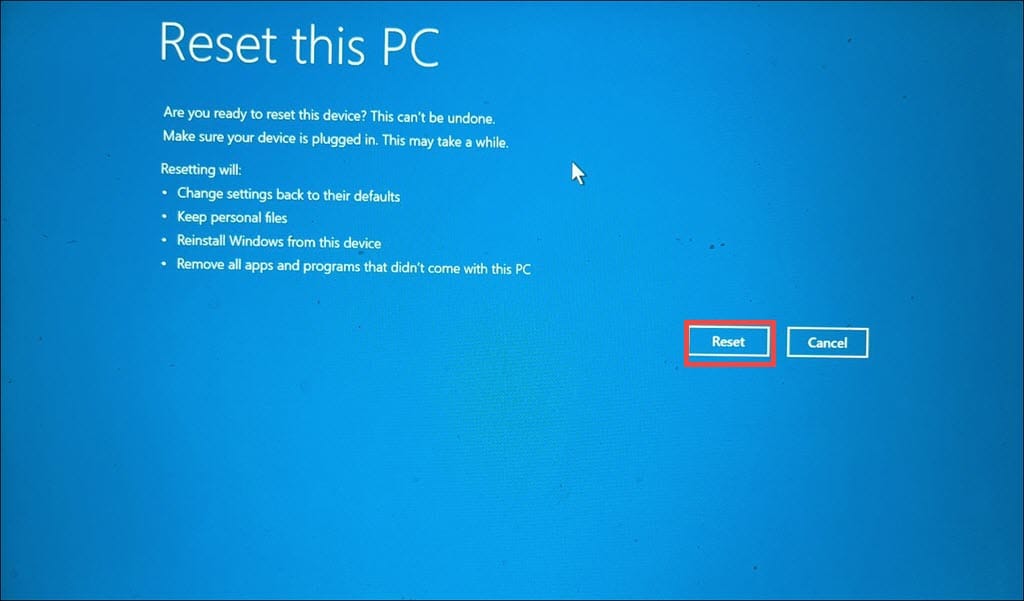
- Click the Reset button.
You may also be interested in:
Summary
In this guide, I listed various effective methods to troubleshoot and resolve the 0x0000002F INSTRUCTION_BUS_ERROR in Windows. Starting with basic preliminary checks and advancing to more complex solutions, these steps will help you restore your system’s functionality and stability.
If the problem persists, you’ll need to contact professionals.






User forum
0 messages