Copy Directory Linux - 4 Easy Commands
4 min. read
Published on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help MSPoweruser sustain the editorial team Read more
Thinking about how to copy a directory on Linux? Whether you want to secure crucial data or distribute files, copying directories is a fundamental skill for administrators.
In this guide, I’ll cover some essential commands to perform this operation. Let’s go!
How To Copy a Directory on Linux
1. Press CTRL+ALT+T to open the terminal.
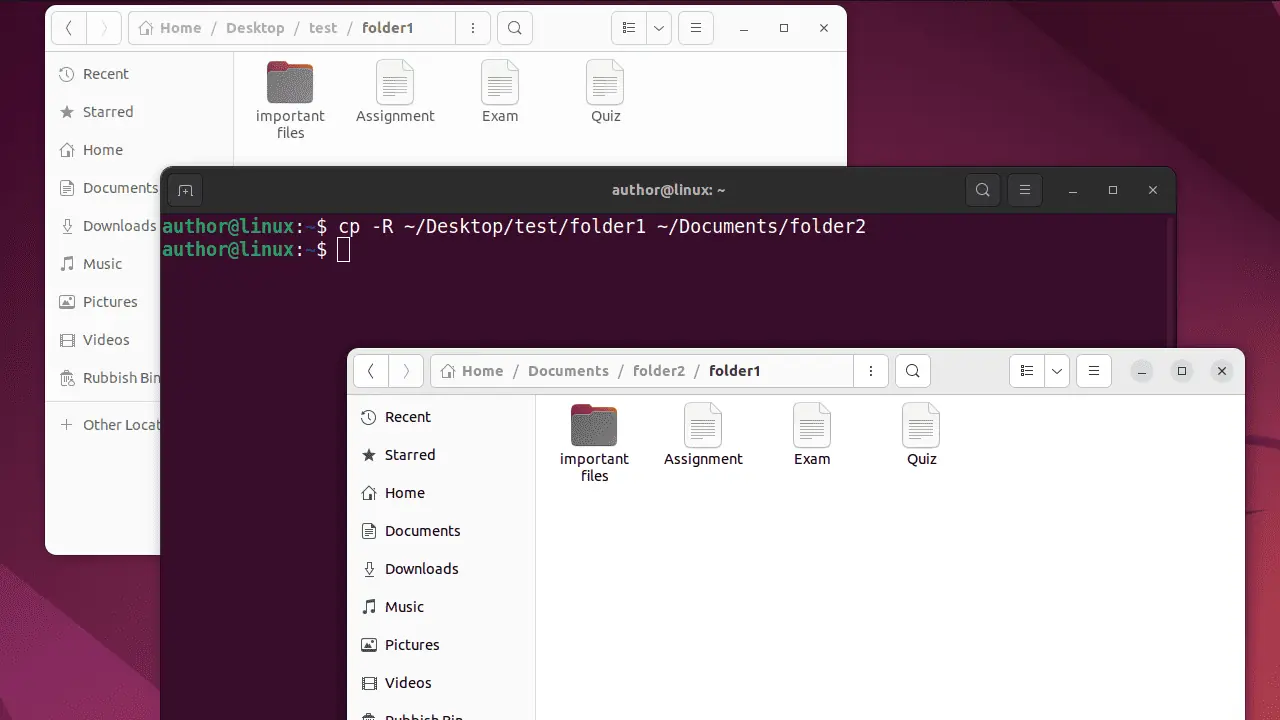
2. Type “cp -R path/to/source/directory /path/to/destination/directory“. In my case, I’ll copy folder1 from “~/Desktop/test” to “~Documents/folder2”.
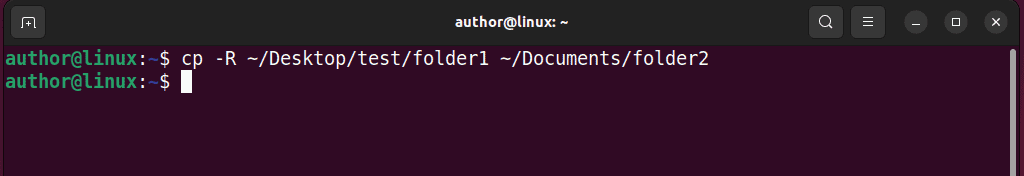
3. For verification, check the content of the destination directory.
How To Copy Multiple Directories on Linux
Let’s explore the following commands to copy multiple directories on Linux:
1. Using the cp Command
In Linux-based operating systems, the cp command is used to copy multiple files and directories. It creates identical copies.
Additionally, you can add the -R or -r option for recursive copying. This option forces the cp command to copy the directories and their entire content, including the subdirectories.
To use this command:
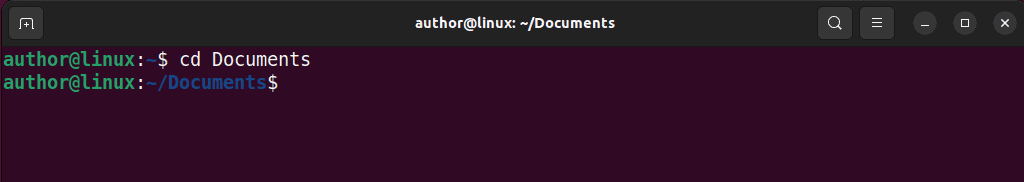
1. First, move to your source directory with cd:
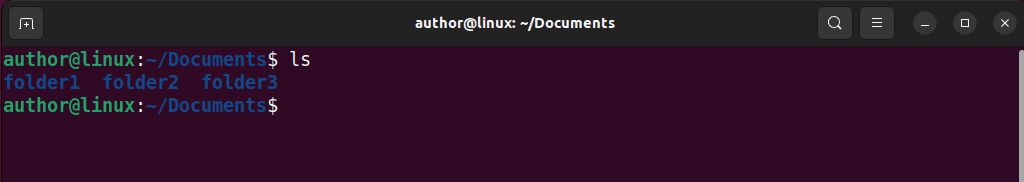
2. Then, execute the ls command to list the content of the working directory:
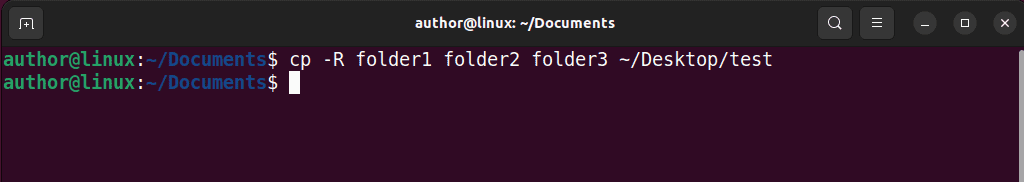
3. Type the “cd -R dir1 dir2 /path/to/destination/directory” command in your terminal. In my case, I’ll create a copy of “folder1”, “folder2”, and “folder3” of the current directory in “~/Desktop/test”.
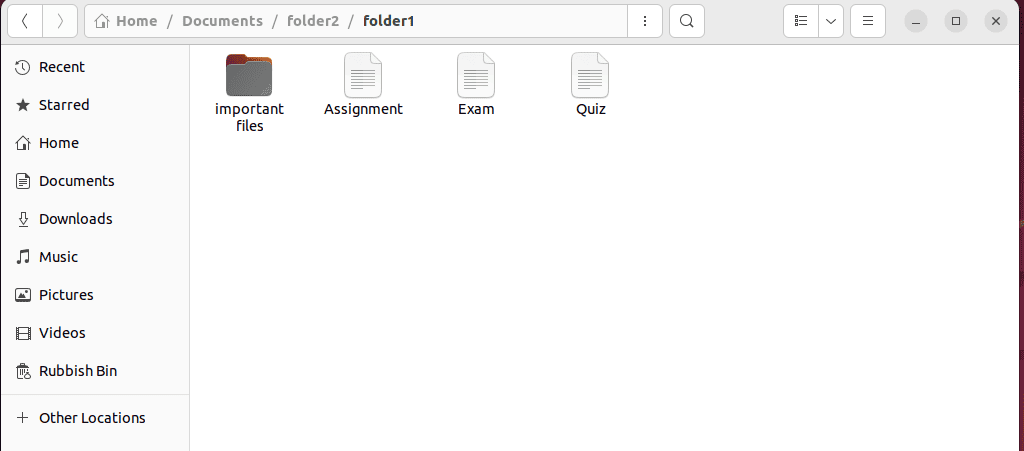
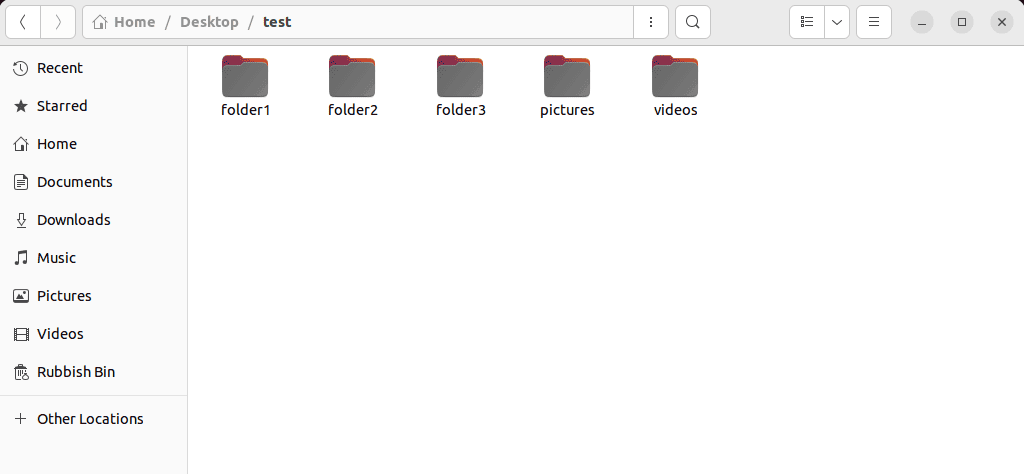
4. Check the destination directory for verification.
2. Using the tar Command
tar is a versatile utility for archiving and copying multiple directories. More specifically, you can utilize it to create a compressed archive of the required directories. Then, extract the content to the desired location.
To do so, add the following options in the tar command (as per requirements):
- -c creates a new archive.
- -z compress or decompress the archive with gzip.
- -v displays the verbose output, showing the files being archived.
- -f specifies the archive file name.
- -x extract files from an archive.
- -C changes to the given directory before extracting files.
Now, to copy multiple directories using tar:
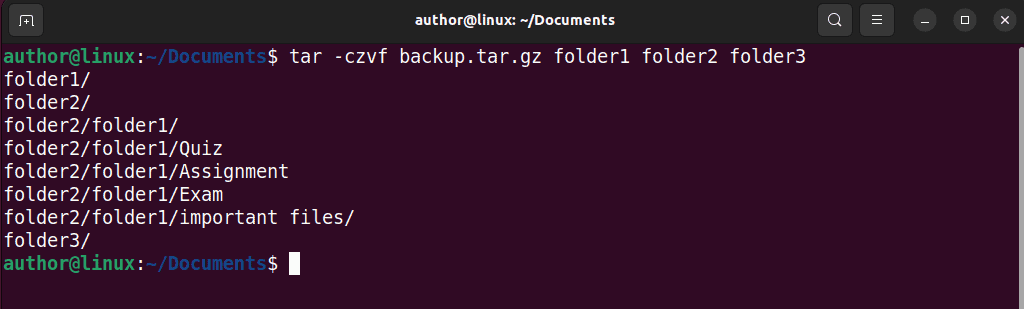
1. First, create a compressed package of multiple directories with “tar -czvf filename.tar.gz dir1 dir2” command.
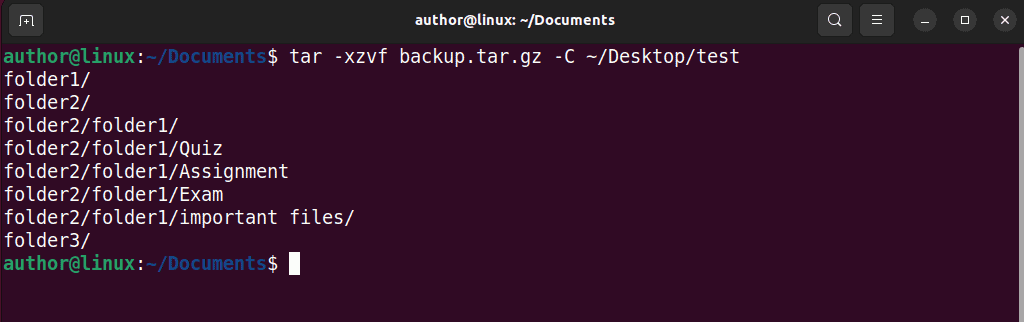
2. Now, extract the compressed package using the “tar -xzvf filename.tar.gz -C /path/to/destination/directory” command.
3. Using the rsync Command
rsync is another well-known utility for directory synchronization. You can use it with the -a option to enable the archive mode. This consequently preserves the permission and attributes of the specified directories.
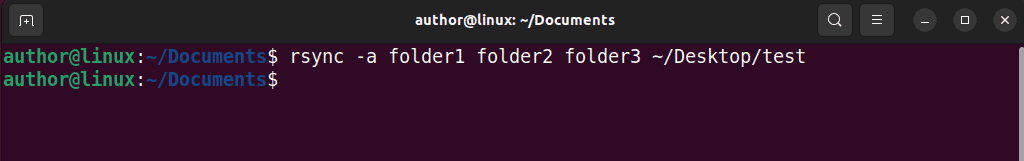
To use it, type “rsync -a dir1 dir2 dir3 /path/to/destination/directory” in the terminal.
How To Copy Directories to Remote Hosts
To copy directories to a remote host, you can use:
- rsync command
- scp command
Prerequisites
1. First, install the SSH server on the remote host with “sudo apt-get install openssh-server“.
2. Start SSH service using “sudo systemctl start ssh“.
3. Enable it with “sudo systemctl enable ssh“.
4. Type “sudo systemctl status ssh” to verify if SSH is active and running.
5. Type “sudo ufw allow 22” to make sure that the Firewall on the remote hosts permits incoming connections on port 22.
Now, you’re ready to copy directories to remote hosts.
Using the rsync Command
Type: “rsync -ar dir1 dir2 user@ip_address:/path/to/destination directory“.
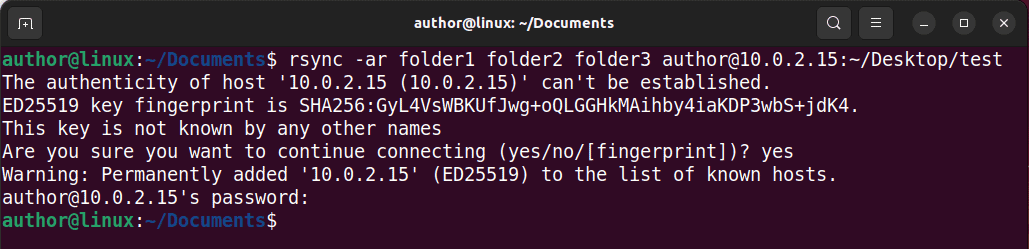
Here, I’ll copy “folder1”, “folder2”, and “folder3” to the “~/Desktop/test” directory of a remote server located at “10.0.2.15” with the “author” username.
Using the scp Command
scp is another command that can copy files and directories between local and remote hosts.
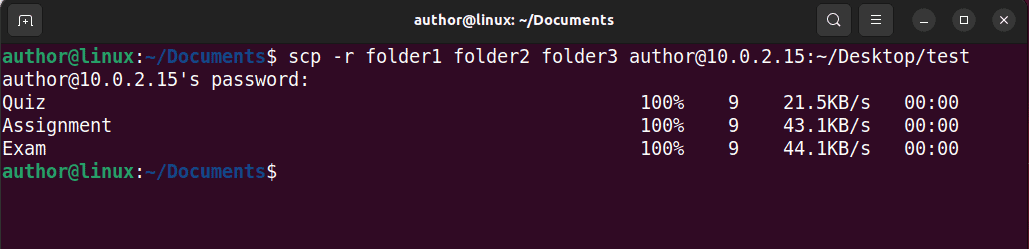
Simply type: “scp -r dir1 dir2 user@ip_address:/path/to/destination/directory“.
You may also be interested in:
- Best SSH Client for Windows – Top 8 Picks for Security
- How to Run Shell Script in Windows
- Ubuntu List Users
So, now you’re familiar with copy directory Linux commands. Most importantly, all of them work perfectly on most of the Linux distributions.
Don’t hesitate to share your favorite method in the comments below!




User forum
0 messages