36 Incredible AI In Healthcare Statistics
13 min. read
Updated on
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help MSPoweruser sustain the editorial team Read more
Once the realm of science fiction, artificial intelligence within healthcare is now a reality. It can help diagnose patients and give treatment recommendations, replace monotonous administrative tasks, and help perform some medical procedures.
The following AI in healthcare statistics gives further insight into the growth of the market, how it is being applied, and attitudes towards it from the public and professionals.
Most Important AI In Healthcare Statistics
These are the core AI healthcare stats everyone needs to know in 2023.
- The AI in healthcare market is estimated to grow to $187.95 billion by 2030.
- A fifth of healthcare organizations have already adopted some form of AI.
- AI could reduce the cost of discovering new drugs by 70%.
- 60% of Americans are uncomfortable with their provider relying on AI.
- Predictive AI tools could reduce hospital admissions by half.
Adoption of AI in healthcare statistics
The following AI statistics look at how wide AI use in healthcare currently is and how it’s being applied.
1. A fifth of healthcare organizations have already adopted some form of AI.
(Source: Statista – AI Adoption)
As of 2021, 19% of surveyed healthcare organizations across the world had adopted AI models for at least 2 years. A further 18% were evaluating whether to implement AI, while 26% had not yet considered it.
2. Clinical trials are the most common use of AI in healthcare.
(Source: Grand View Research – AI Healthcare)
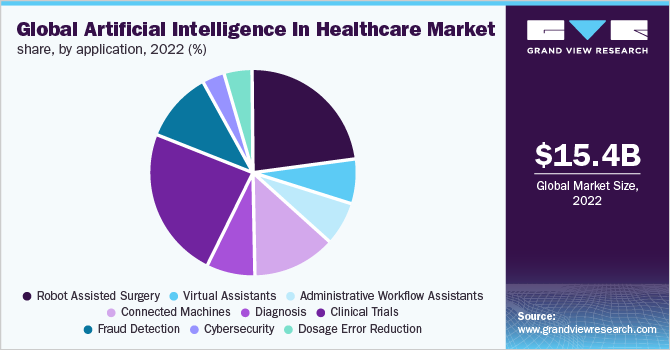
Of all the applications of AI in healthcare globally, clinical trials account for 24.2%. This is closely followed by robot-assisted surgeries, connected machines, and virtual assistants.
3. 34% of AI applications in the NHS are diagnostic.
(Source: HTWorld – AI Applications)
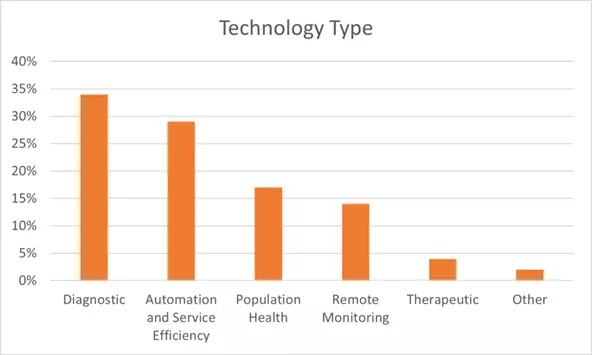
AI is starting to be used in every facet of healthcare, with 34% of NHS use cases being diagnostic. This includes AI-driven image analysis, pathology, and endoscopy. Going forward, AI is going to play a major role in identifying illness and disease in Britain.
The second most common application of AI is automation/service efficiency, followed by population health. The latter is focused on ‘leveraging the strength of AI when dealing with large patient datasets to help predict and prevent diseases in the general population’.
4. All UK stroke centers will have AI stroke diagnosis technology by the end of 2023.
(Source: HTWorld – AI Strokes)
Currently, 86% of NHS stroke treatment facilities are using AI diagnosis tools to speed up detection and treatment. This will be 100% by the end of the year.
This is part of a £21 million AI diagnostic fund that also includes AI technology for chest X-rays to detect lung cancer.
5. Clinicians are the primary users of new AI technology.
(Source: Statista – AI Users)
A 2021 survey found that 88% of healthcare organizations in the final stages of implementing new AI technology intended clinicians to be the primary users, I.e., those dealing directly with patients.
Furthermore, 72% of organizations in the early stages also intended their AI technologies to be used by clinicians.
6. 10% of US healthcare professionals use generative AI tools like ChatGPT or Med-PaLM 2.
(Source: Tebra)
While healthcare has many of its own unique AI applications, individual professionals are also using popular AI content generators like ChatGPT and Med-PaLM2 to answer medical questions. Of 500 surveyed, 1 in 10 professionals said they were doing so and half had plans to try it.
Of healthcare professionals that have used generative AI tools, 95% said they had a positive outlook after seeing the quality of the medical advice generated.
7. AI helped Moderna optimize its COVID-19 vaccine.
(Source: Financial Times)
Moderna used an AI model trained on 20,000 unique mRNA sequences to help design and manufacture its first batch of COVID-19 vaccine for testing in just 42 days. AI shows great promise in speeding up the drug discovery and clinical trial process.
Financial AI in healthcare statistics
AI in healthcare is already a billion-dollar market. These financial statistics look at market share, estimates for the future, and other fascinating financial data.
8. Adoption of AI in healthcare could save between 5% and 10% in US spending.
(Source: NBER)
AI creates efficiency, which means fewer wasted dollars. Research suggests wider adoption within healthcare could significantly cut spending, which was between $200 billion and $360 billion in 2019.
9. The AI in healthcare market is estimated to grow to $187.95 billion by 2030.
(Source: Statista – AI Healthcare Market)
The global AI in healthcare market was last valued at $11 billion in 2021 and is estimated to be worth nearly $188 billion by the end of the decade. That’s a compound annual growth rate of 37%.
In comparison, the AI in education market is only expected to reach $20 billion by 2027.
10. Robot-assisted surgery could be valued at $40 billion by 2026.
(Source: Harvard Business Review)
Of 10 applications that could significantly change healthcare, AI robots for surgery is valued the highest ($40 billion by 2026). Virtual nurse assistants were ranked second ($20 billion), which will free up nurse workload and counter labor shortages.
11. North America generated the most revenue from AI in healthcare in 2022.
(Source: Grand View Research)
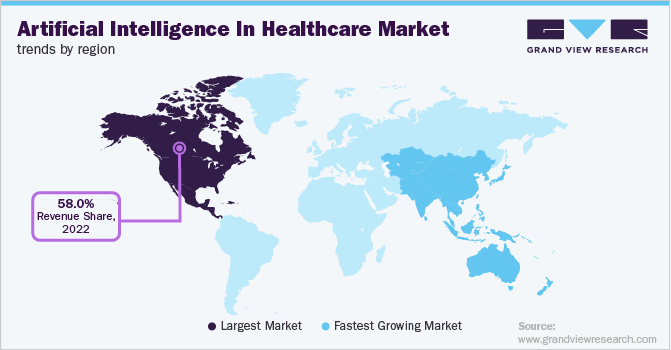
From a revenue perspective, the US is responsible for the most revenue generated by AI in healthcare. In 2022, it had a 58% share of the market, followed by the Asia-Pacific region with 40.9%. China and Australia are among the fastest-growing AI healthcare markets.
12. The AI in healthcare market is dominated by 6 corporations.
(Source: Grand View Research)
The key 6 corporations involved in AI for healthcare are: IBM, NVIDIA, Nuance Communications, Microsoft, Intel, and DeepMind Technologies. This includes healthcare-specific technology and general AI solutions that the industry has found useful.
13. AI could reduce the cost of discovering new drugs by 70%.
(Sources: Insider Intelligence, Financial Times)
The early phase of drug discovery is a tireless process of reading and analyzing scientific literature and calculating and testing drug interactions. AI can automate much of this and save billions of dollars in the process. In turn, this can drive down the end cost of drugs too.
Funding for AI drug discovery rose 3,800% between 2016 and 2021.
14. AI could make savings of $16 billion due to medicine dosage errors.
(Source: Harvard Business Review)
When humans must make an educated decision about the dose of medicine a patient receives, it can have costly consequences. At best, a dose that is too high costs more in volume. At worst, the incorrect dose can result in adverse effects, leading to costly corrective procedures and further care.
15. The AI in precision medicine market is expected to reach $14.5 billion by 2030.
(Source: Grand View Research – AI Precision Medicine)
Precision medicine is an approach to healthcare that takes into account individual variability in genes, environment, and lifestyle when diagnosing and treating diseases. AI’s ability to quickly handle vast amounts of data and learn as it goes will help precision medicine become the norm.
The market was valued at $1.27 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 35.7%, reaching 14.53 billion in 2030.
Patient attitudes towards AI in healthcare statistics
The public is naturally fearful of new technology, but there are still some positive attitudes toward AI for cancer screening, therapy, and reducing ethnic biases.
16. 60% of Americans are uncomfortable with their provider relying on AI.
(Source: Pew Research)
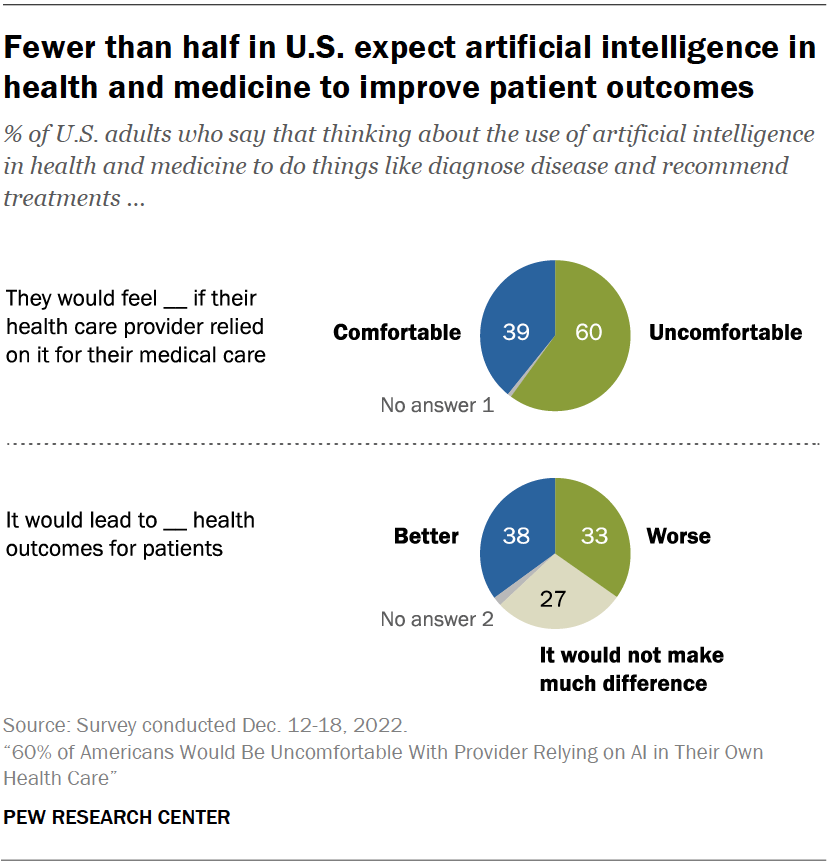
A recent study of 11,004 US adults found 6 in 10 are uncomfortable with the idea of their healthcare provider relying on AI to make a diagnosis or recommend treatments. This may be because many do not believe AI will improve outcomes.
17. 60% of Americans also believe AI will not improve health outcomes.
(Source: Pew Research)
While 38% of respondents did believe using AI would improve health outcomes, 33% thought the opposite, and 27% didn’t think it would have any impact. There are also concerns about how AI would be implemented.
Other worries are that AI would worsen the patient-provider relationship (57%) and that it would be a security risk for patient records (37%).
18. 75% of Americans believe AI in healthcare will be implemented too quickly.
(Source: Pew Research)
For much of the public, the concept of AI has only popped up in recent years. This could play into fears that it is being adopted too quickly in healthcare. Even those that have heard a lot about AI, 70% still believe the healthcare industry will move too fast and not fully understand the risks to patients.
19. Half of US adults who believe there is an ethnic bias in healthcare think AI will level the playing field.
(Source: Pew Research)
One positive outlook from the research comes from those who believe healthcare is biased on racial and ethnic grounds. I.e., worse outcomes for ethnic minorities. 51% believe that using AI to make decisions will eliminate that bias. 15% think it would explicitly make biases worse.
20. 65% of US adults would either definitely or probably want AI to be used in skin cancer screening.
(Source: Pew Research)
Skin cancer screening is one area the public feels AI would help, with 55% believing it might even be more accurate than traditional screening. Interestingly, educated young men were the biggest AI supporters, while uneducated minorities tended to be more fearful of such an application.
21. 1 in 4 Americans would prefer to talk to an AI chatbot than a human therapist.
(Source: Tebra)
First, it was telephone therapy, then messaging apps. Now an increasing number of people are turning to AI chatbots including ChatGPT for therapy without any human involvement. AI therapy is now so popular, 40% of Americans prefer it over visiting a real therapist in person.
22. UK adults are most concerned with AI making diagnoses.
(Source: iNews)
A survey of 2,000 UK adults revealed the most pressing concern about AI in healthcare is relying on it to make diagnoses (39%). Allocating medicines was 27%, and enhancing surgical procedures was 17%.
On the other hand, 26% believed the most useful application was supporting healthy lifestyles, followed by reducing waiting times.
23. 28% of UK adults would support AI in healthcare if shown evidence of improved outcomes.
(Source: iNews)
When asked what would alleviate concerns about AI in healthcare, the highest percentage of respondents (28%) said proof of improved patient outcomes. This evidence is already starting to grow but may need better dissemination for the public.
Professional attitudes towards AI in healthcare statistics
Despite fears of AI job losses, those in healthcare generally have a positive outlook on how AI will benefit the industry.
24. 72% of healthcare leaders trust AI to support nonclinical, administrative tasks.
(Source: Optum)
Trust in AI depends on its application. The majority of surveyed healthcare leaders are all for using AI for nonclinical, administrative processes that take away time clinicians could be spending with patients.
However, they are less excited about virtual patient care (41%), diagnosing and predicting outcomes (40%), and medical image interpretation (36%).
25. Nearly 78% of British NHS professionals believe AI is useful in their field.
(Source: Frontiers)
Of more than 7,500 National Health Service professionals, 77.79% said AI would be useful or extremely useful in their area of work. This included medical doctors, nurses, therapists, and managers.
Only 10% are worried AI could replace their role entirely.
26. 94% of healthcare executives believe they have a duty to use AI responsibly.
(Source: Optum)
The healthcare industry is more than aware of public concerns about AI and healthcare executives believe it is their duty to ensure it is deployed responsibly.
27. 96% of healthcare executives believe AI is important for health equity.
(Source: Optum)
Of 500 leading hospital executives surveyed, nearly all of them believe AI is important for reaching their health equity goals. I.e., delivering a fair and unbiased service to everyone.
28. More than 75% of European radiologists believe AI algorithms are accurate for diagnosing patients.
(Source: SpringerOpen)
Of the 30% of radiologists that already use AI in Europe to help diagnose their patients, the majority find the results to be reliable. 16.8% specifically consider it unreliable, while 7.5% had no opinion on the matter.
The future of AI in healthcare statistics
What will the AI healthcare landscape look like in the future and what does the data say about the potential benefits?
29. Predictive AI tools could reduce hospital admissions by half.
(Source: Forbes)
A study by Clare Medical found that by using an AI tool to predict which elderly patients are more likely to experience ‘medical events’, measures could be put in place to reduce hospital admissions. This cuts costs, saves lives, and frees up hospital beds for other non-preventable emergencies.
30. AI models can predict cancer patient survival with 80% accuracy.
(Source: UBC)
Researchers at the University of British Columbia developed an AI model that can take oncologist notes, identify patient characteristics, and predict cancer survival with 80% accuracy.
This allows health providers to make earlier referrals to support services or offer more aggressive treatments, with the hope of improving outcomes.
31. AI can rule out suspected heart attacks twice as fast as humans.
(Source: NIHR)
A recent trial by NIHR and the British Heart Foundation was able to significantly increase the efficiency of heart attack care. CoDE-ACS was able to rule out a heart attack in twice the number of patients, compared to humans, with 99.6% accuracy.
This ensures they are sent home or given alternative care, while staff are freed to care for patients who are at higher risk.
32. AI can detect early signs of dementia as accurately as humans.
(Source: Sheffield University)
An AI tool called CognoSpeak is able to analyze the language and speech patterns of patients and detect Alzheimer’s with 90% accuracy – the same as traditional methods. This could improve the speed and efficiency of diagnoses as there’s less reliance on human doctors.
33. Counterfactual algorithms are as accurate as the top 25% of doctors.
(Source: Nature Communications)
AI has had success with associative algorithms, which identify diseases that are strongly correlated with a patient’s symptoms. However, correlation does not always mean causation.
A counterfactual algorithm that uses causal reasoning was shown to be as accurate as the top 25% of doctors, compared to the top 44% when using associative algorithms.
34. Oncology and Neurology will dominate AI-based precision medicine.
(Source: Precedence Research)
In 2022, oncology (cancer diagnosis) generated more than 31% of the revenue share for the AI in precision medicine market. This along with a rise in neurological disorders like epilepsy and dementia, is expected to dominate the market over the next decade.
35. AI robot surgery could reduce the length of patient hospital stays by more than 20%.
(Source: Harvard Business Review)
A study of orthopedic surgeries found that an AI robot reduced complications by five times compared to unassisted surgeons. This could also result in a 21% reduction in the length of patient hospital stays following surgery.
Subsequent savings are estimated at $40 billion per year.
36. AI nurse assistants could reduce maintenance tasks by 20%.
(Source: Harvard Business Review)
AI-powered nurse assistants are estimated to save $20 billion a year by reducing the time nurses spend on maintenance tasks for patients by 20%. An example of this is Sensely’s “Molly” chatbot, which asks patients questions, assesses symptoms, and directs them to the appropriate service.
Conclusion
These AI in healthcare statistics reveal an already booming industry that will only grow in the years to come. While there are some concerns from patients, professionals believe it will cut costs, reduce human biases, and improve patient outcomes.
Research reveals how AI can be as accurate or better than humans at analyzing symptoms and predicting outcomes. This will speed up diagnosing and treating patients.
This along with the broader application of AI to administrative tasks will make healthcare much more efficient in the future.
Sources
- Statista – AI Adoption
- Grand View Research – AI Healthcare
- HTWorld – AI Applications
- HTWorld – AI Strokes
- Statista – AI Users
- Tebra
- Financial Times
- NBER
- Harvard Business Review
- Insider Intelligence
- Grand View Research – AI Precision Medicine
- Pew Research
- iNews
- Optum
- Frontiers
- SpringerOpen
- Forbes
- UBC
- NIHR
- Sheffield University
- Nature Communications
- Precedence Research


User forum
0 messages