35 AI Recruitment Statistics for Employers and Candidates
Recruitment is one of the most important aspects any business can undertake. The rise of AI has the potential to make it more efficient, less biased, and cut HR costs. However, it’s not without concerns too.
These AI recruitment statistics explore the rate of adoption, the different ways AI is being applied, public and corporate attitudes, and what the future could hold in the age of artificial intelligence.
AI Recruitment Statistics: Top Picks
These are some of the most important AI recruitment stats everyone should know in 2023.
- 88% of companies globally use some form of AI technology in HR including recruitment.
- About 79% of recruiters think AI will be sophisticated enough to make full recruiting and firing decisions.
- 95% of recruiters believe AI could be beneficial for the application process.
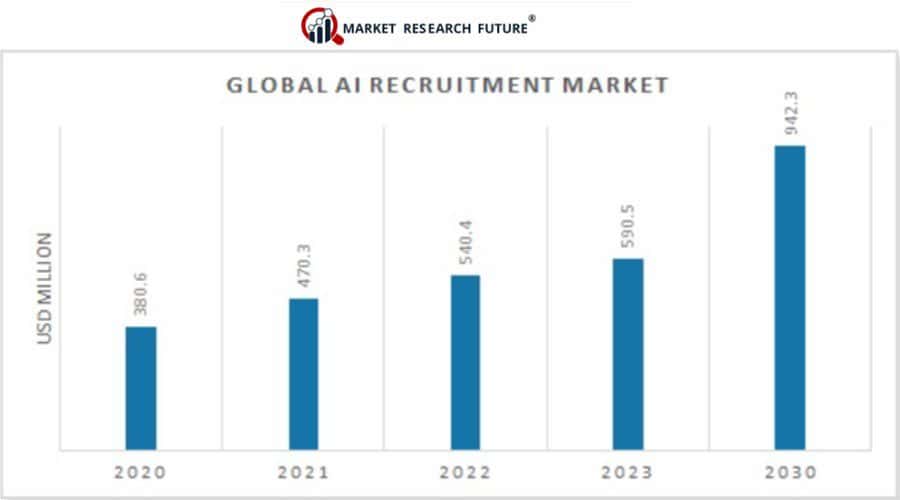
- The global AI recruitment market will reach $590.5 million by the end of 2023.
- By 2030 the global AI recruitment market is expected to reach $942.3 million.
- 35% of recruiters think AI could overlook unique and unconventional talent.
Adoption and Usage of AI for Recruitment
The following AI recruitment statistics look at the current and emerging landscape of AI automation in HR and hiring.
1. 88% of companies globally use some form of AI technology in HR, including recruitment.
(Sources: Mercer 1, 2, The Guardian)
China has set the bar with 100% of major firms using some degree of AI and automation within HR, including some recruitment tasks. The US is close behind with 83% of companies doing the same. In Australia, a third of businesses currently use AI tools in recruitment.
Altogether approximately 88% of global companies have adopted AI in HR.
2. 41% use AI chatbots to engage with candidates during recruitment.
(Source: Mercer 2)
Of the above companies that have adopted AI, 41% use AI chatbots as part of the recruitment process. E.g., answering candidate queries or completing questionnaires. 40% also use AI to screen and assess candidates.
3. 44% use AI to filter the best candidates based on information available on the internet like social media profiles.
(Source: Mercer 2)
Although the practice of viewing candidate social media profiles is somewhat controversial, many companies are applying AI to identify the best candidates based on their digital footprint.
Proponents say it is just as much about looking for positive traits rather than those old college party photos.
4. Early AI recruitment adopters have seen their cost per screening candidate reduced by 75%.
(Source: Ideal)
With the cost of screening candidates reduced by up to 75%, it’s no surprise AI recruitment software is rapidly growing. The same data shows a 4% increase in revenue per employee, and employee turnover decrease by 35%, due to hiring more suitable candidates.
5. Adoption of AI in recruitment succeeds the most with close collaboration between HR and IT.
(Source: Gartner – AI in HR)
Of those companies that successfully implemented AI for HR tasks like recruitment, 41% indicate close collaboration between HR and IT as one of the main reasons it worked.
Meanwhile, 35% pointed to having a sufficient amount of data for the AI to access, and 32% cited a well-articulated strategy.
6. Hilton reduced the time it takes to fill vacant positions by 90%.
(Source: Recruiting Daily)
Hilton adopted AI tech in its hiring process to optimize acquiring high-level talents. The software analyzed personal candidate info and related data, and improved hiring rates by 40%. Most impressive was a reduction in vacant position replacement times by 90%.
AI Recruitment Statistics for Market and Financials
How big is the AI recruitment market and what can other financial data tell us about this growing technology? These AI statistics have the answer.
7. The global AI recruitment market will reach $590.5 million by the end of 2023.
(Source: Market Research Future)
In 2022, the size of the AI recruitment market was $540.4 million. This is predicted to rise to $590.5 million by the end of 2023. The ability to automate the screening of talent, save time, and cut costs, are all key drivers in the growth of AI recruitment.
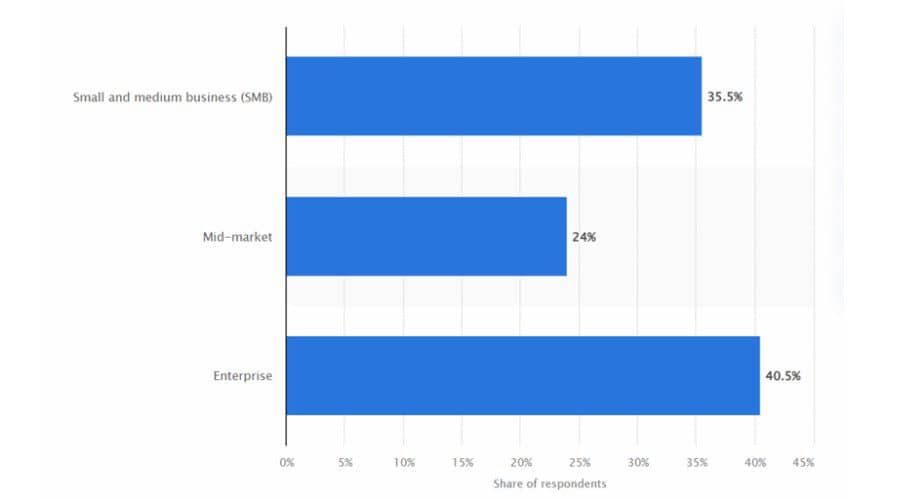
8. Enterprise businesses spend the most budget on AI recruitment.
(Source: Statista – AI Recruitment Budget)
The share of companies that allocate budgets to AI recruiting tools worldwide is led by Enterprises (40.5%), Small & Medium sized businesses (35.5%), and Mid-markets (24%).
9. HR technology including AI is the top investment priority among HR leaders in 2023.
(Source: Gartner – HR Investment)
Nearly half (46%) of HR leaders say new technology is the top investment priority in 2023. This includes AI-driven recruiting and screening capabilities and candidate relationship management platforms.
The second priority is general staffing and recruiting initiatives, such as solving talent shortages and recruiting technologies.
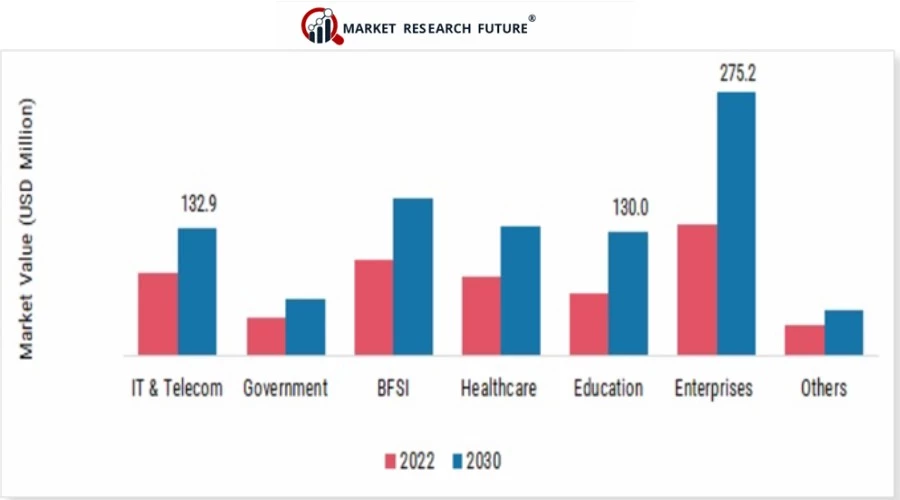
10. By 2030 the global AI recruitment market is expected to reach $942.3 million.
(Source: Market Research Future)
With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.9% for 2023-2030, the market is expected to grow from $590.5 million to more than $940 million.
Enterprise businesses account for both the largest growth and overall largest market share for this period, reaching $275.2 million. The Banking, financial services and insurance sector, Healthcare, Education, and IT & Telecoms, are all expected to exceed $130 million each.
11. The Asia-Pacific region will lead the global AI recruitment market in 2030.
(Source: Market Research Future)
By 2023, the Asia-Pacific region led by China will be the AI recruitment market leader, approaching $400 million. North America follows, accounting for $323.2 million of the market value.
12. North America cut the most costs using AI recruitment in 2022.
(Source: Market Research Future)
North America was able to cut recruitment costs by 40% in 2022 by using AI. Europe followed with a 36% reduction and the Asia-Pacific region with 25%. This is because AI recruitment leader China had already made huge cost savings in prior years.
The rest of the world combined made savings of 20%.
Attitudes Towards AI Recruitment Statistics
These stats explore how the public, employees, and recruiters feel about the adoption of AI.
13. AI is seen as a viable solution due to the inefficiencies in current recruitment.
(Source: Greenhouse)
Typically, 45% have rejected jobs after bad interviews, and 46% of new hires fail to meet standards. This is one reason why AI helps with the recruitment process and is seen as a solution worth exploring by businesses of all sizes.
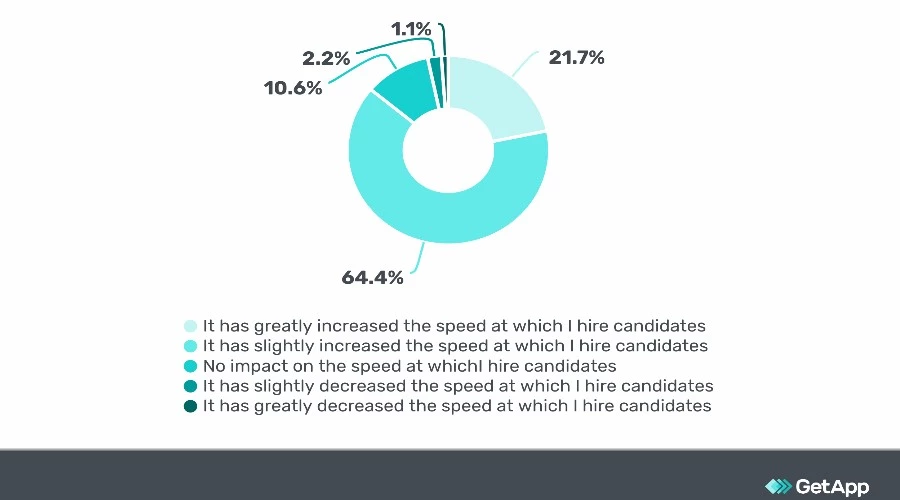
14. 86.1% of recruiters believe using ATS machine learning speeds up the recruitment process.
(Source: GetApp)
ATS uses a sub-field of AI known as machine learning that can handle vast quantities of data. Leaving this to humans is considerably time-consuming, but the majority of recruiters that use AI believe it speeds up the process considerably.
15. More than 78% say it improves the quality of candidates hired.
(Sources: GetApp, McKinsey)
Ultimately, recruitment is about finding the best candidate for the job. The majority of those who use AI say it does indeed help them hire a better quality candidate.
AI is able to reduce a human recruiter’s subjective opinion of a resume because AI algorithms only consider factors that improve predictive accuracy. It will take the candidate’s name, experience, qualifications, and personal statements and pick only those that its data says are most likely to match high performance on the job.
16. About 79% of recruiters think AI will be sophisticated enough to make full recruiting and firing decisions, but candidates disagree.
(Source: Tidio)
Based on survey data from over 10,000 recruiters, 79% think AI technology will advance to the point where it doesn’t just screen candidates but will make the hiring and firing decisions with little human input.
Conversely, candidates themselves believe this is less likely. Only 43% agree with recruiters. Moreover, 69% of candidates would not agree to AI alone making the decision to hire them.
17. 63% of recruiters believe screening candidates can be replaced by AI.
(Source: Statista via DemandSage)
Currently, recruiters believe the area that AI could replace traditional recruiting the most right now is screening candidates (63%). This is followed by Searching for a candidate on different platforms (56%), Creating job descriptions (64%), and conducting initial interviews (37%). Could recruiting itself join the list of AI job losses?
18. 41% of American adults oppose AI reviewing job applications.
(Source: Pew Research – AI Hiring)
While more candidates oppose AI making the final hiring decision, a solid 41% also oppose AI reviewing job applications. Only 28% are in favor, while 30% are not sure.
19. The majority of recruiters believe AI could be beneficial for the candidate application process.
(Source: Tidio)
95% of HR respondents believe AI could aid candidates during the application process. For example, using chatbots to answer queries or guide them through the process.
20. 68% of recruiters believe AI will help remove human biases from the process.
(Source: Tidio)
With growing awareness of unintended biases during recruitment, nearly 70% of recruiters think AI can remove these issues and make recruitment fairer. After all, if a human isn’t making the decision, their prejudices cannot change the outcome.
However, there are still concerns about a lack of human involvement.
21. However, only 2 in 5 say their AI vendors are clear about how their tools prevent or avoid biases.
(Source: Talent Insight)
Despite a positive outlook by most, 59% of companies that have bought AI tools from vendors say these vendors aren’t transparent about the measures taken to prevent discrimination or biases.
22. 20% of black Americans think AI recruitment will actually make racial bias worse.
(Source: Pew Research – AI Racial Bias)
While the majority of all ethnicities surveyed believe AI recruitment will reduce instances of human bias, 20% of black respondents actively think it will make things worse.
When including the 32% who think it won’t make a difference, that’s more than half of black American adults that are skeptical of AI removing racial bias from the hiring process.
On the other hand, Asian Americans make up the largest percentage (64%) of any ethnicity that believe AI will help reduce racial bias
23. More Americans feel AI would do a bad job of spotting a candidate’s social suitability.
(Source: Pew Research – AI Hiring)
Survey respondents believe AI would be worse than humans at identifying a candidate’s social suitability. I.e., which applicants would or wouldn’t work well with their co-workers (43% worse/ 17% better).
24. Similarly, 35% of recruiters think AI could overlook unique and unconventional talent.
(Source: Zippia)
Not everyone fits the typical mold that would make a good candidate and AI might not be able to use human judgment, despite being better at filtering vast numbers of candidates.
Because of this, there are concerns that excellent but unconventional talent could slip through the net because the ‘computer says no’.
25. 67% of recruiters believe saving time is the key benefit of using AI.
(Source: Statista – AI Benefits)
According to 67% of hiring decision-makers, the key benefit of using AI for recruitment is time-saving. Moreover, it can find the best candidates, save money, and remove biases.
26. 22% of HR employees feel necessary human interactions have been lost.
(Source: Mercer 2)
With a lot of general HR and recruitment tasks going online and being subject to AI automation, existing employees expressed concern that some necessary human interactions have disappeared in favor of bot responses and computer decisions.
This suggests fears of a soulless workplace and the potential to lose the benefits of human conversation that could incorrectly filter out good candidates.
27. British workers want full disclosure about AI in recruiting and no AI job interviews.
(Source: Total Jobs)
A survey of more than 2,000 UK workers about AI being used in the recruitment process shows positive attitudes. The caveat, however, is that 72% believe full disclosure of how the technology is being used should be mandatory. Moreover, 86% say they do not support AI conducting job interviews in place of traditional face-to-face interviews.
28. Only 3% of University Relations and Recruiting (URR) professionals plan to use AI.
(Source: National Association of Colleges and Employers)
Skepticism is much higher in certain sectors of the workforce. For example, just 25% of URR employers say they use AI for recruitment. Moreover, just 3% plan to use AI in the next year.
Among those that did use AI for recruitment, it was only to help write emails to candidates and refine interview questions. No decisions were made by the AI in terms of hiring.
29 Senior HR professionals believe it takes 3 years to properly implement AI.
(Source: People Management)
Of 600 UK-based HR managers and directors surveyed, the majority saw benefits in AI. However, 40% said it would take at least 3 years before their firms would be prepared for the impact of this technology.
Common concerns included over-dependence on AI, and security and privacy.
AI Recruitment Research and the Future
Looking ahead to the future, these AI recruitment stats and facts explore the latest research and important findings.
30. AI could reduce gender and other biases for roles like Police Chief.
(Source: Stanford)
When recruiters were hiring for a Police Chief role, the majority chose men without college degrees over women with college degrees because they felt men had more ‘street smarts’. However, when the same applications were given female names, human recruiters still chose the men because they had those college degrees.
The research proposed that AI would avoid this gendered bias and only choose the candidates that are legitimately fit for the role.
31. AI is better at picking candidates for corporate boards.
(Source: Harvard Business Review)
AI has been shown to be a valuable tool in corporate governance, particularly in the selection of board members. Research by the Fisher College of Business found that traditional board selections were more likely to be male with large networks and multiple directorships.
In contrast, the AI algorithm selected boards that were more diverse in terms of gender, background, and experience. Directors who aren’t part of the ‘old boys club’ and come from different backgrounds do a better at monitoring management and providing valuable insights into corporate policy that are usually overlooked.
32. Bad AI training can lead to bad recruitment outcomes.
(Source: BBC News)
Of course, an AI recruitment tool is only as good as the data it is trained on, even if it can learn from it faster and more accurately hat humans.
In 2018, a hiring tool used by Amazon was found to be biased because its algorithm favored male candidates. This was because most applicants were male and the AI assumed this meant men were more suitable, slowly downgrading female candidates that were just as suitable on paper.
33. But biases in AI can be mitigated to produce better results than humans.
(Source: Artificial Intelligence Review)
Research in 2022 found that well-crafted AI makes hiring more efficient, fills roles quicker, and predicts candidates more likely to be hired following the interview process.
The research also found AI was better than humans at hiring people that would go on to have long-term success within a company.
Moreover, AI recruitment produced more diverse hires than humans who are plagued by internal biases.
34. AI can coach you on how to best apply for job listings.
(Source: Financial Times)
AI within the hiring sphere is not just on the recruiter’s end. Technology, such as that offered by job search engine Adzuna, uses AI to prep you for your chosen role.
It generates relevant interview questions, so you can tell how prepared or suitable you really are before applying.
35. AI can tailor your CV to specific jobs.
(Source: Kickresume)
New AI tools are popping up every day to help candidates craft their CVs for certain roles. These include Skillroads, Kickresume, and Rezi.
The CV scanning roadblock that filters out candidates (perhaps even good ones) based on key terms is now being used against recruiters.
Conclusion
There is no doubt from these AI recruitment statistics that technology can help make numerous aspects of hiring more efficient. However, there are more concerns among candidates and the public than recruiters and companies themselves.
Nonetheless, the market for these types of tools is set to continue to grow considerably over the next decade. During this time, AI is likely to become much more accurate and attitudes may change.
Sources
- Mercer 1
- Mercer 2
- The Guardian
- Ideal
- Gartner – AI in HR
- Recruiting Daily
- Market Research Future
- Statista – AI Recruitment Budget
- Gartner – HR Investment
- Greenhouse
- GetApp
- McKinsey
- Tidio
- Statista via DemandSage
- Pew Research – AI Hiring
- Talent Insight
- Pew Research – AI Racial Bias
- Zippia
- Statista – AI Benefits
- TotalJobs
- National Association of Colleges and Employers
- People Management
- Stanford
- Harvard Business Review
- BBC News
- Artificial Intelligence Review
- Financial Times
- Kickresume
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help MSPoweruser sustain the editorial team Read more




User forum
0 messages